HIPROX
A flexible pressurized facility for the development of novel combustion concepts
Kontaktperson
Hear Mario Ditaranto talk about the HIPROX facility.
Novel power technologies as oxy-fuel or pre-combustion CO2 capture for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, demand new combustion concepts. Development of cleaner and more efficient combustion systems requires tailoring of flame features at microscopic level to extend stability and emission performances.
Specification
Measurement capabilities
- Flame visualization (chemiluminescence, high speed)
- Multi-species emission (>15 species, FTIR)
- Temperature, heat flux
- Pressure (static and dynamic)
Pressure vessel
- 15 bar
- 4 optical accesses
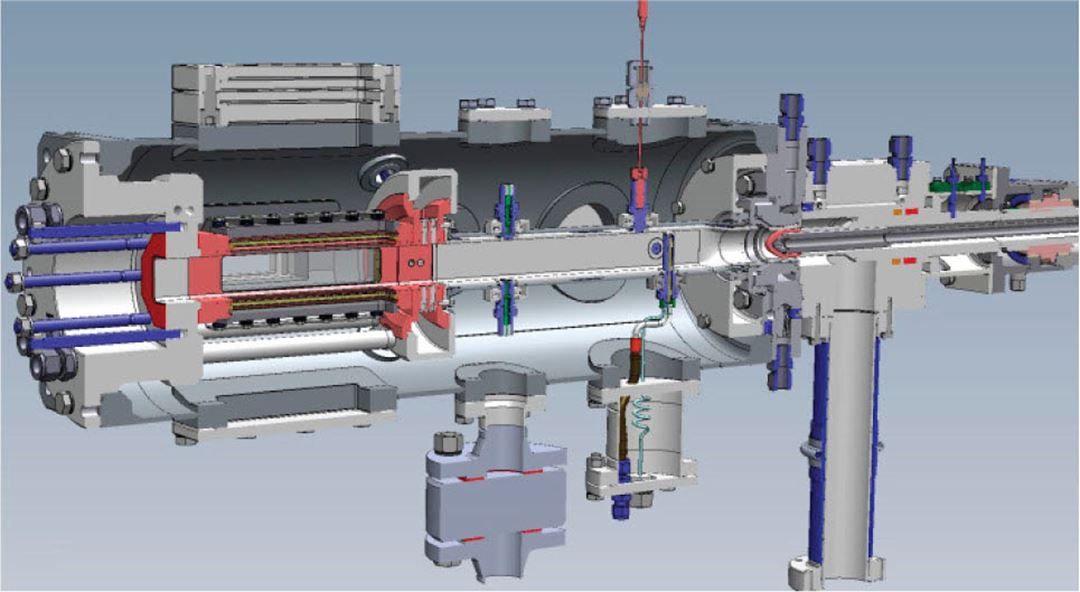
Combustor section
- 10 bar
- Double wall quartz flame section
- TBC coated dilution section
- Modular setup, 3 flame sections existing: 40X40 mm2; Ø 50 mm ; Ø 90 mm
Fuel
- Max power 150 kWth
- Two feed lines 3 g/s (main) and 1.4 g/s (pilot) methane
- Storage: cylinder battery
Oxidizer
- Two independent heated feed lines PN 40
- Air 30 bar – 520 kg/hr - 300°C – Boosted network
- CO2 15 bar - 300 kg/hr - 300°C - 6 m3 liquid tank
- O2 20 bar - 72 kg/hr - 20°C - Cylinder battery

Why CCS?
The purpose of CO2 capture and storage (CCS) is to minimize CO2 emissions and prevent large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) from being released into the atmosphere. SINTEF conducts research on the whole value chain for CCS.
SINTEF leads the national Centre for Environment-friendly Energy Research (FME) on CCS - NCCS
