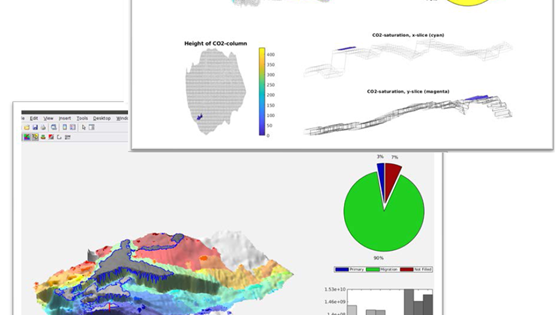
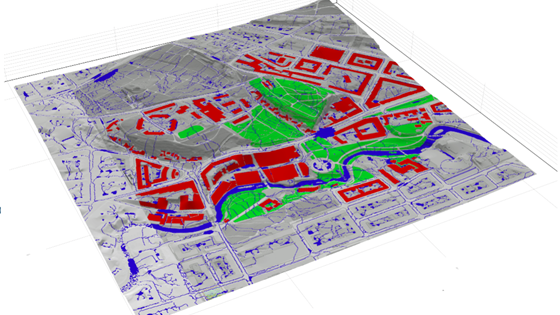
Our Expertise
We offer expertise in developing and applying advanced computational methods for complex modelling and simulation problems. We specialize in creating new algorithms and transforming them into efficient, reliable, and robust software of professional quality.
How Do We Work?
We are applied mathematicians and computer scientists who, over many years, have built deep expertise in our application areas. We combine this with a strong drive to develop methods and software that can be adapted to various applications without compromising accuracy or performance.
We draw on a strong tradition at SINTEF Digital, where the development of numerical methods, algorithms, and high-quality software has been central since the early 1990s. Our goal is to create solutions that not only meet today’s needs but are also capable of handling tomorrow’s challenges. Our broad methodological expertise enables us to contribute effectively across a wide range of fields and technology areas.
What Sets Us Apart?
We combine high academic standards with a deep understanding and strong focus of industrial needs, ensuring that our solutions are both innovative and practical. What sets us apart is our ability to swiftly advance new ideas from academic research, overcoming simplifying assumptions, use our open-source software to rapidly prototype and demonstrate effectiveness in relevant environments, and bringing new research into operational use.
International Orientation
Our group is internationally oriented and consists of 19 permanent scientists, most with a PhD in mathematics or physics, and several associated master and PhD students. We have established strategic cooperations with leading academic institutions worldwide and long-lasting partnerships with international industry clients.
With over 20 years' experience, we combine high academic quality in research with a strong focus on industrial relevance.
Key Achievements
- Numerous publications in leading journals and conferences each year demonstrate our academic strength and international position at the forefront of research.
- Over two decades of developing high-quality, open-source, community software that is widely used by researchers and industry worldwide. Our tools make advanced simulation accessible and contribute to global knowledge sharing and innovation.
- Proven track record in developing simulation technologies that are in operational use, such as the OPM Flow reservoir simulator, the multiscale formulation in SLB's INTERSECT MS SFI, and the GPU Ocean simulator. This highlights our ability to take research from theory to practical application in demanding industrial settings.
- Long-standing experience with hardware accelerators (e.g., GPUs). We were pioneers in applying GPUs to scientific computing and continue to explore emerging technologies to stay at the forefront of innovation.
Strategic Directions
To meet the future needs of our users, we have in recent years initiated research on differentiable simulators, optimization under uncertainty, integrated physics-and-data-driven methods, and practical use of quantum computing.
We are also exploring what the future of human interaction with computational models might look like by combining applied mathematics, simulation technology, and artificial intelligence. Our vision is to develop natural, conversational interfaces with simulators that allow users to set up models, seamlessly combine different simulators, analyze results, and improve simulations supported by technologies such as large language models (LLMs), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and AI agents, in combination with differentiable simulators.
Building on our long tradition of developing flexible and generic methods, we are now working to make simulation tools more intuitive, efficient, and intelligent—across disciplines.
How We Can Help You?
- Need advanced simulation tools for oil & gas, CO2 storage, or geothermal energy? We offer deep expertise across a wide range of methods and can quickly bring new ideas to life using our flexible, open-source frameworks (MRST, OPM, and JutulDarcy). Our tools are designed for rapid prototyping and testing in industry-relevant environments.
- Looking for a next-generation multiphysics simulator that blends data-driven and physics-based modeling? We develop fully differentiable, efficient, and adaptable simulation tools that compute sensitivities with respect to all parameters—ideal for model calibration, uncertainty quantification, and process optimization across disciplines. We also bring decades of experience in hardware-accelerated computing.
- Curious about the potential of GPUs or quantum computing? We design methods that leverage cutting-edge hardware—from GPUs and compute clusters to emerging quantum technologies. We can help you evaluate whether these platforms are right for your needs and how they might deliver significant performance gains.
- Want to make advanced simulation tools easier to use? We explore how to automate complex workflows and create intuitive user experiences. Our work includes developing conversational interfaces that let you interact with simulators as if they were expert collaborators—making modeling more accessible and efficient.
- Need help with something not listed above? Our wide-ranging expertise allows us to support many types of challenges. Get in touch, and we will quickly determine whether we—or others at SINTEF—are the right match.
Join Us
We are always open to new collaboration opportunities. Contact us to learn more about our research and how we can work together to solve complex scientific and technological challenges. You can also engage with our expertise through tailored courses, strategic consulting, or by spending time with us as a visiting researcher or collaborator.