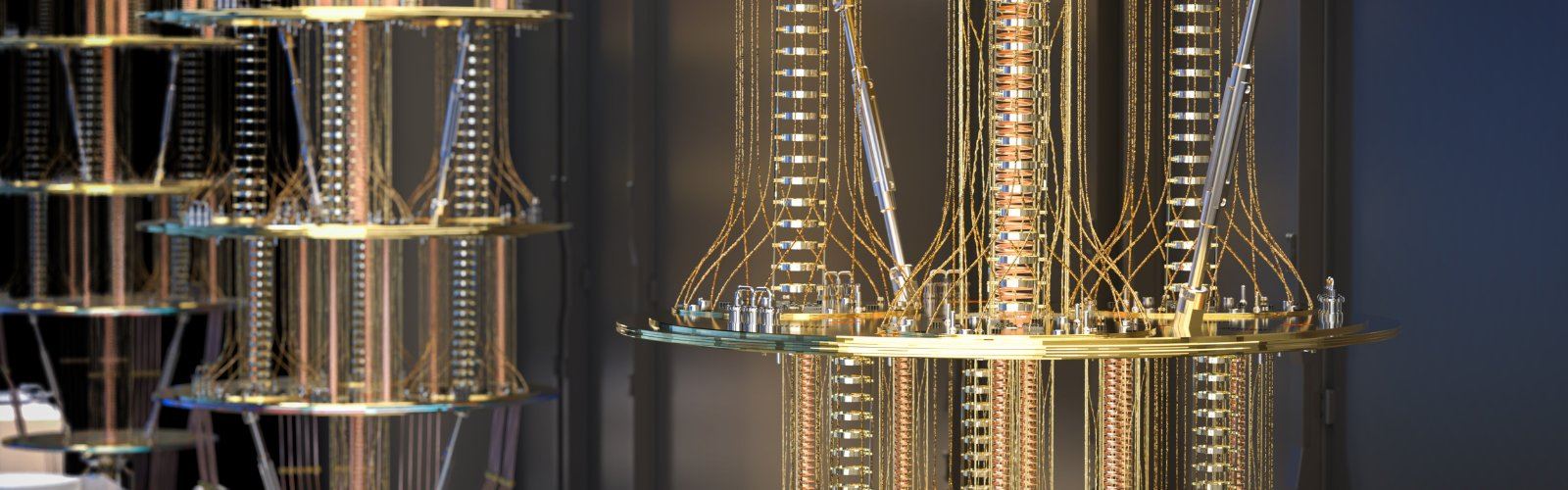
A hundred years after quantum mechanics first revealed how the world is connected on an atomic scale, we are now in the midst of the second quantum revolution.
Quantum physics has been a crucial factor in technologies such as computers, mobile phones, high-speed internet, and solar cells. Researchers have since managed to manipulate quantum properties directly, and now we are at the beginning of a new quantum leap. Combined with artificial intelligence, this will provide us with opportunities we could previously only dream of.
The United Nations has declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, and there is now an international race to master this field.
With our coordinating role in the Gemini Center for Quantum Technology and the Center of Excellence CC-NorChip, as well as our central role in the Norwegian Quantum Cluster and several projects within quantum sensors and quantum computing, SINTEF is a major player in the national collaboration that is making Norway quantum-ready.
SINTEF already possesses expertise in this field, and we have a solid foundation for further research in quantum technology. Our professional environments are strong in areas such as computation, communication systems, and artificial intelligence—and our research in sensor technology is world-leading.
Additionally, our infrastructure, including the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology (MiNaLab), is central to Norway's success in the quantum initiative. This infrastructure is part of the lab collaboration NorFab, which consists of NTNU, UiO, USN, and SINTEF. The collaboration recently received funds from the government and the Research Council for equipment that makes it possible to take new steps in quantum research.
SINTEF also has advanced characterization laboratories and is a key partner in the national characterization infrastructures NORTEM and NICE, which can be utilized to characterize materials for quantum technology applications.
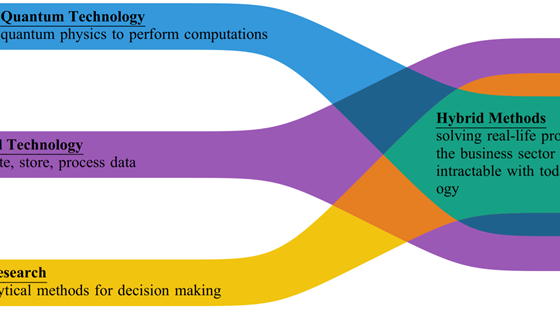
At SINTEF, we believe there are three areas where Norway has particularly good opportunities to develop cutting-edge expertise in quantum technology:
Quantum Computing
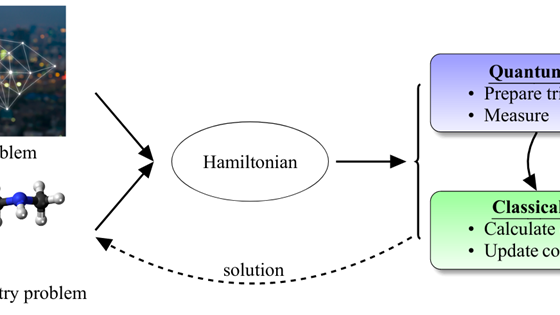
A fundamentally different way of performing calculations that could potentially help us discover new medicines and materials, solve logistical challenges, and perform calculations impossible for classical computers to handle. For instance, we have already developed various quantum algorithms that can help solve large optimization challenges with quantum computers. We are mapping, evaluating, and developing use cases where quantum computers can potentially outperform purely classical methods through ongoing collaborative projects with our industry partners. We are also working on how to use quantum computers in a high-performance computing (HPC) setting.
Quantum Sensors
Will enable us to perform measurements with unprecedented accuracy. Quantum phenomena are extremely sensitive to the environment and can provide us with measurement instruments of fantastic precision. Quantum sensors for magnetic fields and acceleration, for example, have numerous applications related to security and preparedness and are precise enough to read signals directly from the brain or nerves—which can be used, among other things, to control prosthetics. Detection of individual photons (light particles) is essential for extremely sensitive light detection, and also serves as a key component in many systems for quantum sensing, quantum communication, and quantum computing.
SINTEF coordinates projects such as SiQUEST, where we are developing quantum-based sensors for pressure in collaboration with UiO, Kongsberg, and Justervesenet. We have also launched the strategic internal project QSENS, which aims to develop improved single-photon detectors with higher operating temperatures and good time resolution. QSENS involves collaboration with the University of Oslo, the Norwegian Metrology Service, Kongsberg, and the universities of Warwick and Augsburg.
Read more about some of our research in this field in this scientific article published in Nature Photonics.
Quantum Communication
Society and businesses are exposed to cyber-attacks daily. Quantum communication can help us by providing methods that make communication lines eavesdropping-proof and prevent confidential information from being intercepted. In the long term, quantum communication will become a central part of the future internet, providing us with a much more secure internet than we have today.