Examples demonstrating how our research portfolio contributes to the SDGs
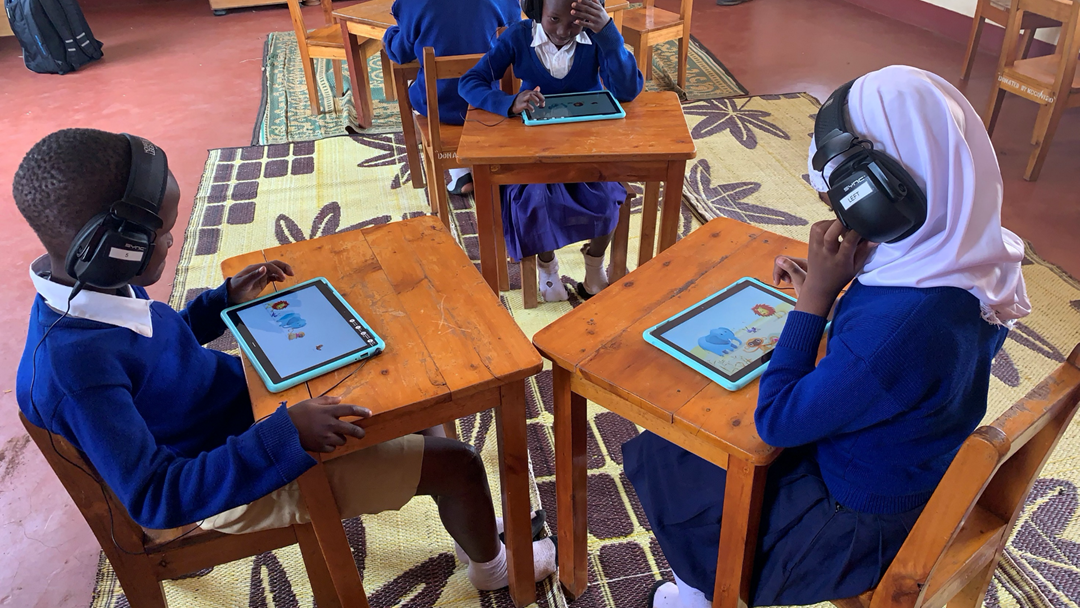
GOAL 1 No Poverty: I Hear You - Gaming technology for testing children's hearing

Using gaming technology, tablets, and headphones, the I Hear You project has developed new tools for testing of children's hearing in schools in Tanzania. The aim is to include children with hearing loss in school and education, and thereby reduce poverty. The project has screened children from three primary schools. The prevalence of hearing loss varied between 7-16 per cent, and the most common causes of hearing loss were earwax and otitis. If hearing loss is detected early, it might be treated with preventive measures and proper medical follow up, thus reducing the number of children dropping out of school.

GOAL 2 Zero Hunger: ProSeaFood - Kelp on a plate

Global food production faces major technological and environmental challenges that must be resolved to become sustainable. The ProSeaFood project is developing prototypes of food products containing processed kelp. The products are being evaluated based on their sensory properties, nutritional content and health promoting effects. The project is also working on methods for processing kelp into food ingredients on an industrial scale. Long-term efforts are being made to launch new products in the Spanish and Norwegian markets.

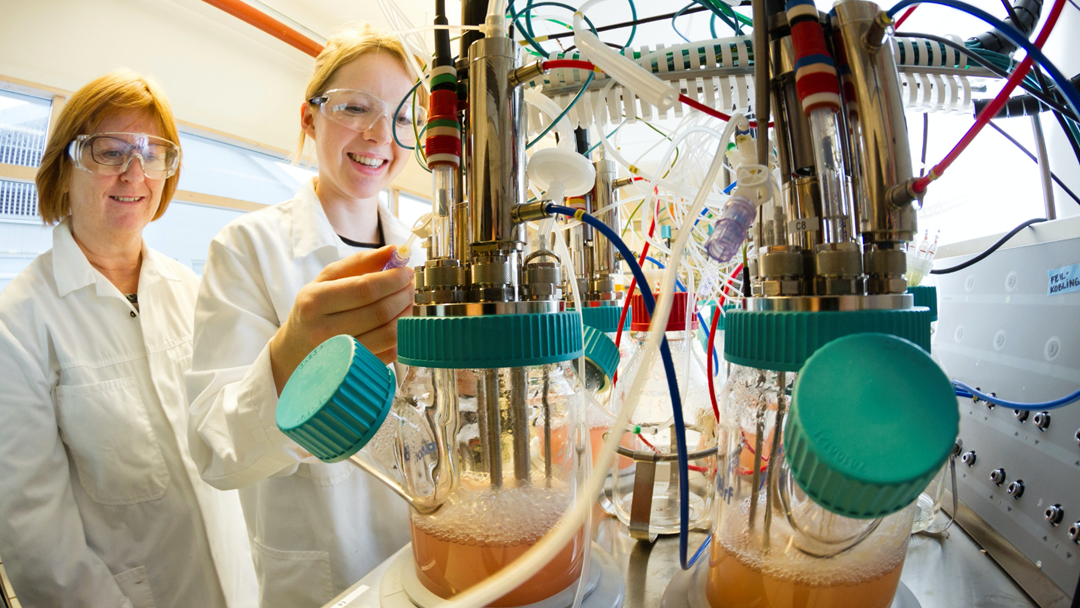
GOAL 3 Good health and well-being: MEDPROT - production of Antibodies

MEDPROT aims to establish production of therapeutic proteins in Norway. The project is focusing on monoclonal antibodies that can be used in treatment of, for example, cancer. The production takes place in cell cultures and the goal of the project is to understand and develop this process in order to improve product yield and quality. Producing antibodies better, faster, and cheaper will help to make this type of medicine available to a larger proportion of the world's population.

GOAL 3 Good Health and Well-being: Social Health Bots - for an effective health service for young people

The concept behind Social Health Bots is that web-based chatbots will lower the threshold for young people to ask questions and seek help in relation to their mental health. This will improve young people's access to reliable information and support, and thus contribute to more effective services. The services may also be a gateway to more comprehensive healthcare services. Evaluations of current prototypes have produced promising results and show that young people benefit from healthcare chatbots.

GOAL 4 Quality Education: BOOST - A school approach to promote mental health and well-being

The goal of the BOOST project is to create good inclusive school environments to prevent school dropout and ultimately social exclusion. BOOST is working on developing a flexible and preventive school approach that promotes good mental health and can be sustainably integrated into school environments. The approach will be implemented and tested in Norway, Spain, and Poland. The goal is to make an approach which is relevant both nationally and internationally.

GOAL 5 Gender Equality: Insight work for Ung.no

The project involves analysing almost 300,000 questions asked by adolescents using the information and communication channel, Ung.no. The insights obtained from the research work may contribute to a better understanding of what adolescents really are interested in and wondering about. One particularly important finding is that boys seek help far less than girls. This has contributed to Ung.no now focusing more on gender and gender equality, and has raised awareness among the panel members who answer the adolescent's questions.

GOAL 6 Clean Water and Sanitation: STOP-IT - risk assessments and protection of water supplies

The STOP-IT project is looking at how water supplies can be protected from physical threats and cyberattacks. STOP-IT is contributing with an integrated, scalable, and flexible technological platform that has been developed up to at least a level seven on the technology readiness level (TRL) scale. The solutions that are being developed will help operators prioritise risk, develop a realistic approach and plan how to strengthen the protection of physical and digital infrastructure. In the future, this will contribute to secure operational control systems in European waterworks.

GOAL 7 Affordable and Clean Energy: Eco-Solar - greener solar power

The goal of the project is to make solar power even greener. The project has taken a systematic approach to reduce the consumption of valuable resources in manufacturing of solar panels, delivering the same performance as conventional panels. Eco-Solar has also developed a solar panel concept that allows the main components to be disassembled, recycled or reused. Overall, the innovations in the project have reduced the ecological footprint in manufacturing solar panels by 45 per cent, costs by 9 per cent, and the carbon footprint by around 20 per cent.

GOAL 8 Decent Work and Economic Growth: SHOP - a planning tool for hydropower

SHOP is a tool for planning hydropower production one to two weeks ahead to ensure the optimum use of resources. A study by Impello Management and Menon Economics shows that the planning tool has increased the value of the water in Norwegian power reservoirs by 2 per cent, which equates to NOK 6.8 billion over 10 years. SHOP can be used for different river systems and has recently undergone major changes as a consequence of an expanding user group with differing needs.

GOAL 9 Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: Klima 2050 - research into the societal risks associated with climate change

Klima 2050 is a centre for research-based innovation that aims to mitigate the societal risks associated with climate change due to factors such as higher precipitation volumes and flooding. The centre, which is led by SINTEF, carries out research into risk mitigation solutions involving the climate adaptation of buildings and infrastructure, as well as solutions for strengthening the innovation capacity of companies. One pilot project at the centre is the climate adaptation network of the City of Trondheim and Trøndelag County Authority, which is contributing to the implementation of knowledge in all municipalities in the county.

GOAL 9 Reduced Inequalities: LOREWO - Local rehabilitation workshops in Namibia and Zimbabwe

The project is creating jobs, facilitating inclusion and empowering people with disabilities to live independent lives. LOREWO provides wheelchairs and services in Namibia and Zimbabwe. Annually more than 1,000 people with disabilities and their families receive assistive technology, training, follow-up, as well as repair of broken assistive technology. The project is based on experience from Norwegian assistive technology centres adapted to local contexts in low-income countries. LOREWO strive to ensure 'no one is left behind'.
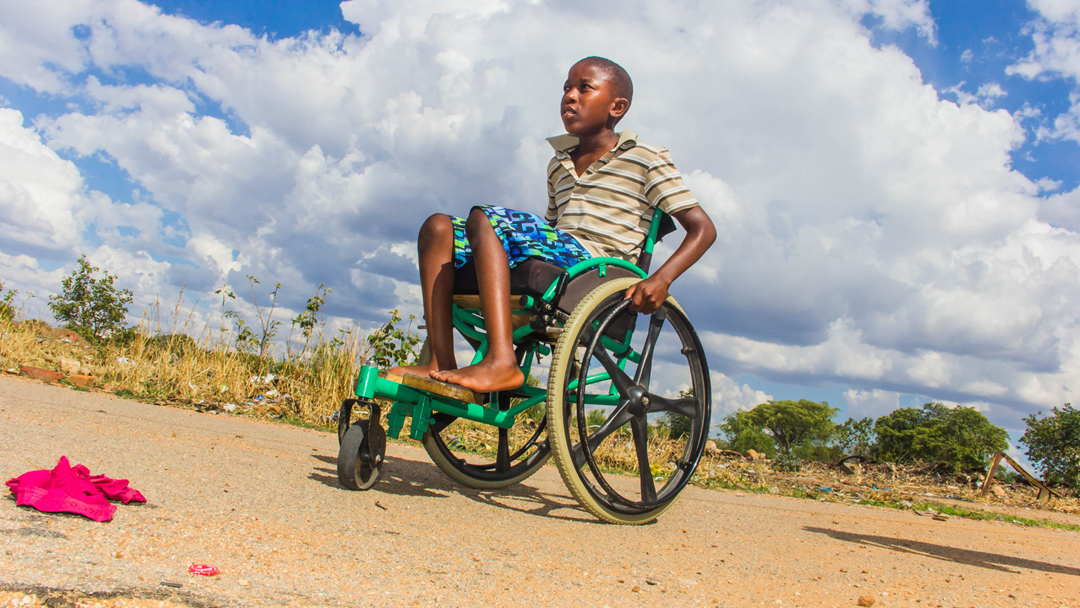

GOAL 11 Sustainable Cities and Communities: FME ZEN - Research Centre on Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities

The goal of the FME ZEN research centre, which SINTEF is part of, is to develop knowledge, solutions, and competitive products. These should contribute to the realisation of sustainable buildings and neighbourhoods with zero greenhouse gas emissions related to construction, operation, and transformation. The centre currently has nine pilot projects spread across Norway. The research conducted in FME ZEN and FME ZEB (Zero Emission Buildings) has demonstrated potential energy savings in the lead up to 2040 of 30 TWh through the active implementation of zero-emission buildings. This is equal to the expected increase in demand for electricity.

GOAL 12 Responsible Consumtion and Production: ConZerW - expertise in waste free construction sites

ConZerW is an innovation project that aims to develop expertise in order to create waste free construction sites. This will be done through process tools that can support professionals in the various phases of the construction process. The tool will contribute to good planning before materials are ordered and efficient assembly in the construction projects of the future. Methods and models will also be developed for analysing material streams and value chains in a flexible manner.
GOAL 13 Climate Action: NCCS - research into CO2 capture, transport, and storage

NCCS is an internationally recognised research centre for eco-friendly energy led by SINTEF. The centre carries out research into various technologies for capturing, transporting, and permanently storing CO2. CO2 management technology facilitates competitive CO2-free products, preserves the value of natural gas, and provides great opportunities for the maritime sector, including CO2 transport via ship. CO2 management may protect 200,000 Norwegian jobs and create 70,000 new ones by 2050 and is a tool for climate-positive solutions.

GOAL 14 Life Below Water: Knowledge and methods to prevent escape of fish

The Prevent Escape research project was initiated to establish the causes of escape incidents at Norwegian aquaculture facilities, develop methods for investigation of incidents, and provide targeted preventative measures for reducing escape of farmed fish. The project has categorized the causes of all escape incidents during 2010-2018, and the knowledge is used to prevent future escape incidents. A website, www.hindreromming.no, has been established to disseminate the results, including short articles, animations and research reports. Fish farmers and employees in the aquaculture industry is the main target group.

GOAL 15 Life on Land: Value creation through increased cooperation between the ocean, agriculture and forest industries

On behalf of Trøndelag County Council, the project has mapped supply volumes and investigated how greater value can be realised from regional bioresources by utilising residual raw materials across the ocean, agriculture, and forestry industries in the region. The work has concentrated on the potential represented by bioprospecting, biorefining, feed production for aquaculture and bioenergy, and the impact new technology can have on the development of new business models. It has identified priority areas that will strengthen business development, employment and contribute to the establishment of green, valuable industry in the region.

GOAL 16 Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions: Information influence activities in the 2019 Norwegian elections

The project investigated whether attempts were made by foreign actors to influence information in connection with the municipal council and county authority elections in 2019. The method is both a quantitative and qualitative analysis of user-generated content from a range of social media and websites that represent political actors, traditional media and 'alternative media'. The materials were also analysed with a view to the dissemination of known 'fake news'. Conspicuous and, to some extent, suspicious communication patterns were detected, although links to foreign actors could not be shown. The entire process rests on advanced 'scraping' (the systematic collection of comments from social media) combined with surveys by Faktisk.no and foreign analyses.

GOAL 17 Partnership for the Goals: Research project on impacts of decarbonisation strategies

The project is part of a partnership between the International Labour Organisation (ILO) and the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). SINTEF is a member of the ILO's Green Jobs Assessment Institutions Network (GAIN) and contributes to improving skills in this type of analysis. SINTEF has investigated the degree to which jobs are affected by different decarbonisation strategies. The project has helped to provide insights into, and knowledge about, jobs and carbon emissions in different sectors in 20 countries in the Latin America and Caribbean region. The numbers relate to sectors and emissions today and in 70 different possible scenarios for 2030 and 2050.
