High Temperature Heat Pumps (HTHP) have been recognized as a promising solution to supply heat at elevated temperatures, which leads to increased system efficiencies and reduced GHG emissions, using potentially emission free electricity.
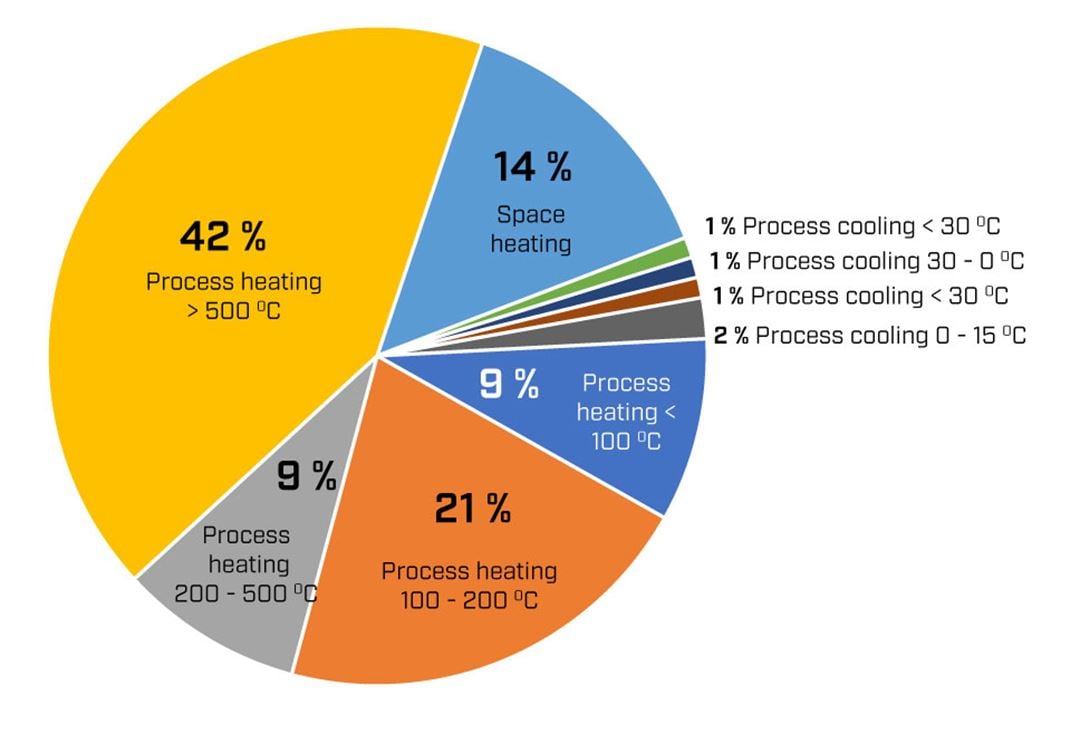
HTHPs are defined as heat pumps providing heat above 100oC, but current commercial systems are limited to around 150oC. The temperature distribution of the industry heat and cooling demand shows the commercial potential for heat pumps as a large part (21%, 508TWh) of the demand lies between 100-200oC, while 67% of this demand is currently covered by fossil fuels.
A development of heat pumps to enable higher supply temperatures will contribute to higher energy efficiencies and electrification of process heating and is thus a vital contribution to the transition towards a sustainable and renewable-based energy system.
Challenges
The current challenges involve large temperature lifts, which limits thermodynamic performances. Specific components, such as the compressor need to be designed to operate at higher temperatures. In addition, high investment costs can result in limited economic performance.
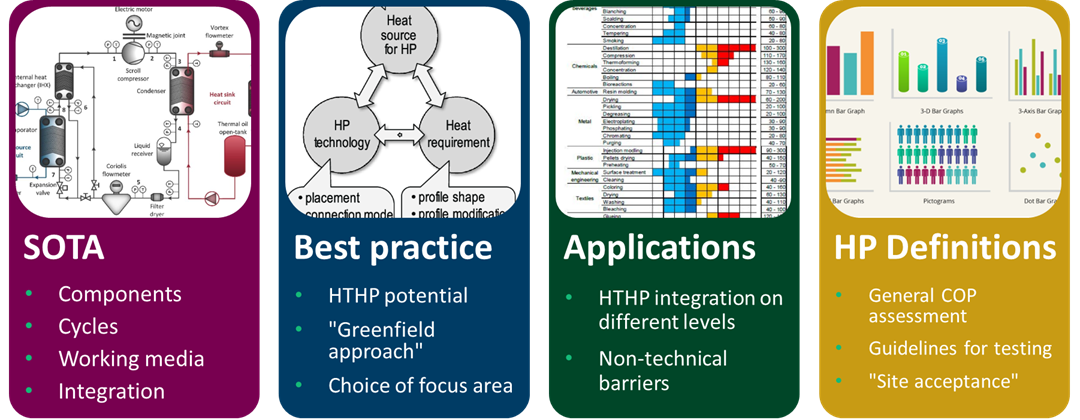
The project is divided into 5 main tasks:
- Technologies – State of the art and ongoing developments for systems and components
- Concepts – Development of best practices for promising application areas
- Applications – Strategies for the conversion to HTHP based process heat supply
- Definition and testing of HP specifications – Recommendations for defining and testing specifications of high-temperature heat pumps in commercial projects
- Dissemination

