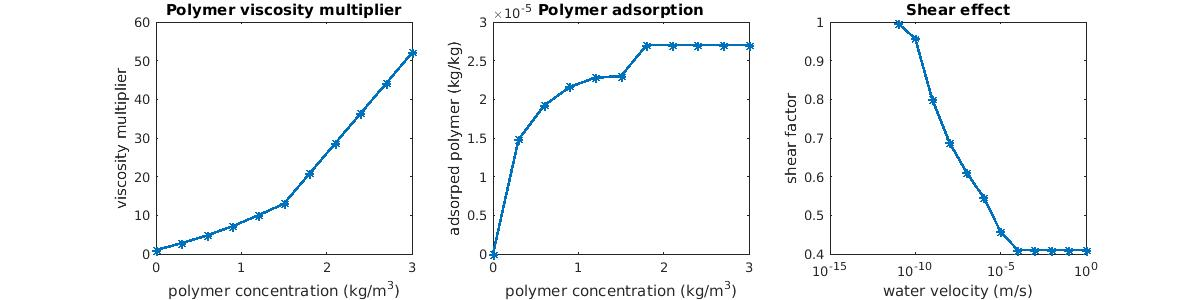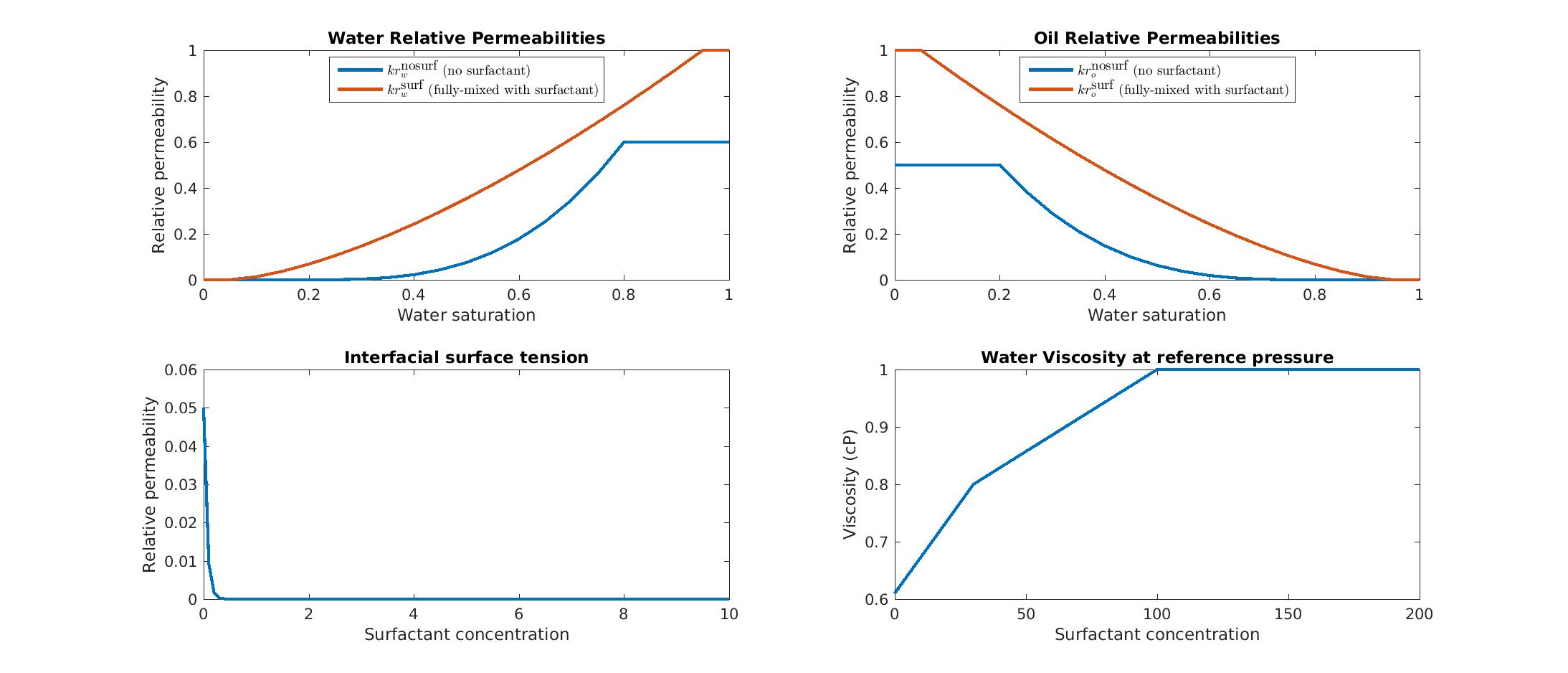|
EOR module
In this module, we provide simulation tools for two water-based enhanced oil recovery techniques, namely polymer and surfactant injection.
Polymer is injected with water to reduce the unfavorable mobility ratio between oil and water, by increasing the water viscosity. Permeability reduction effects also increase the sweep efficiency. Surfactant is used to mobilize immobile oil. The effect of surfactant is essentially modeled through a parametrization of the relative permeability curves with respect to the surfactant concentration. The precise model equations used in the module are almost identical to those implemented in Eclipse 100; see the description notes on the polymer and surfactant models used in MRST. For polymer, the models include
and for surfactant, the models also include
The discretization method is based on a standard two-point flux approximation for the pressure and single-point upstream-mobility weighting for evaluating the flux functions in the mass conservation equations, for each component. The polymer simulator is built on top of a general, three-phase black-oil model, whereas surfactant has only been implemented for an oil-water system. The equations are solved fully implicitly. To do so, we rely heavily on the automatic-differentiation framework and the flexible Newton solver that are readily available from the modules ad-props and ad-core of MRST. The black-oil implementation is taken from the module ad-blackoil. Adjoint computations for optimization can be setup using the optimization module. Examples that are available in this module:
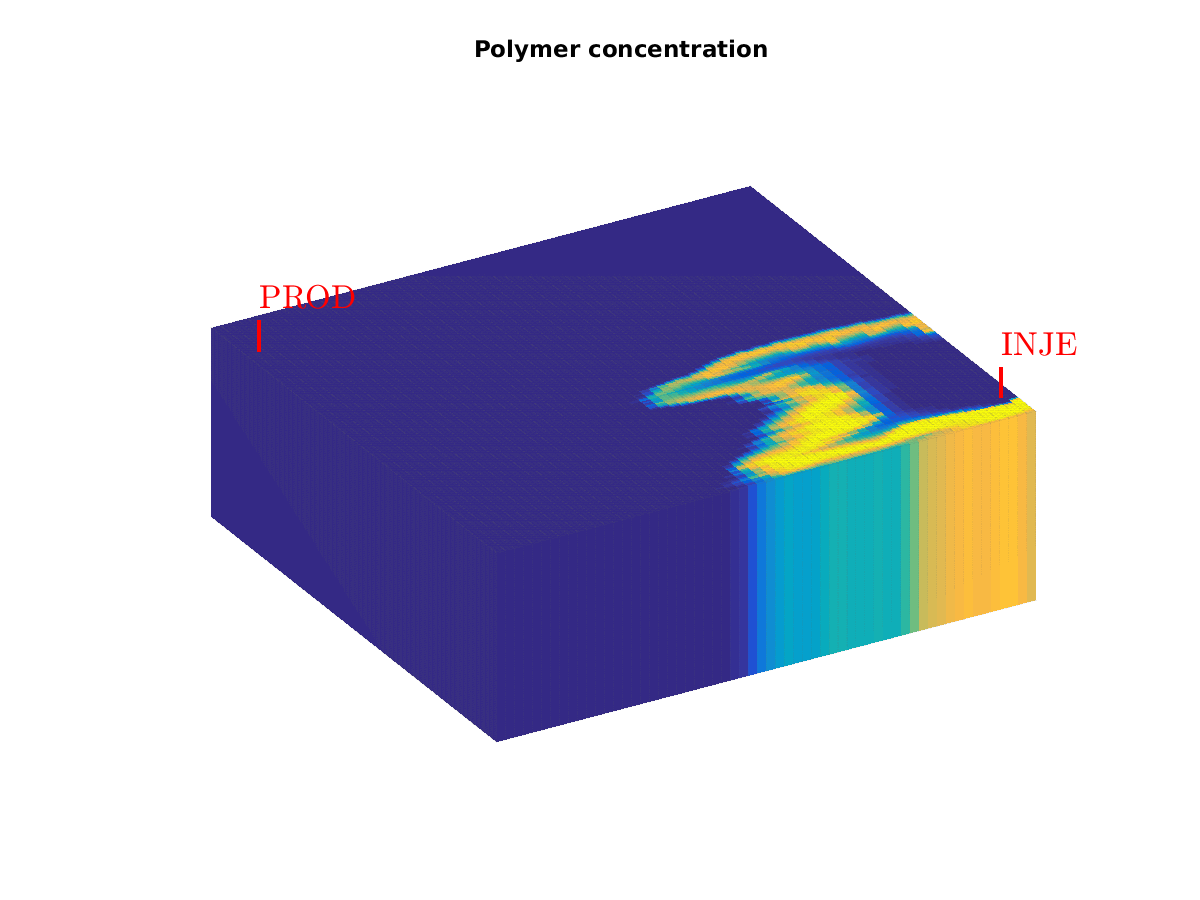
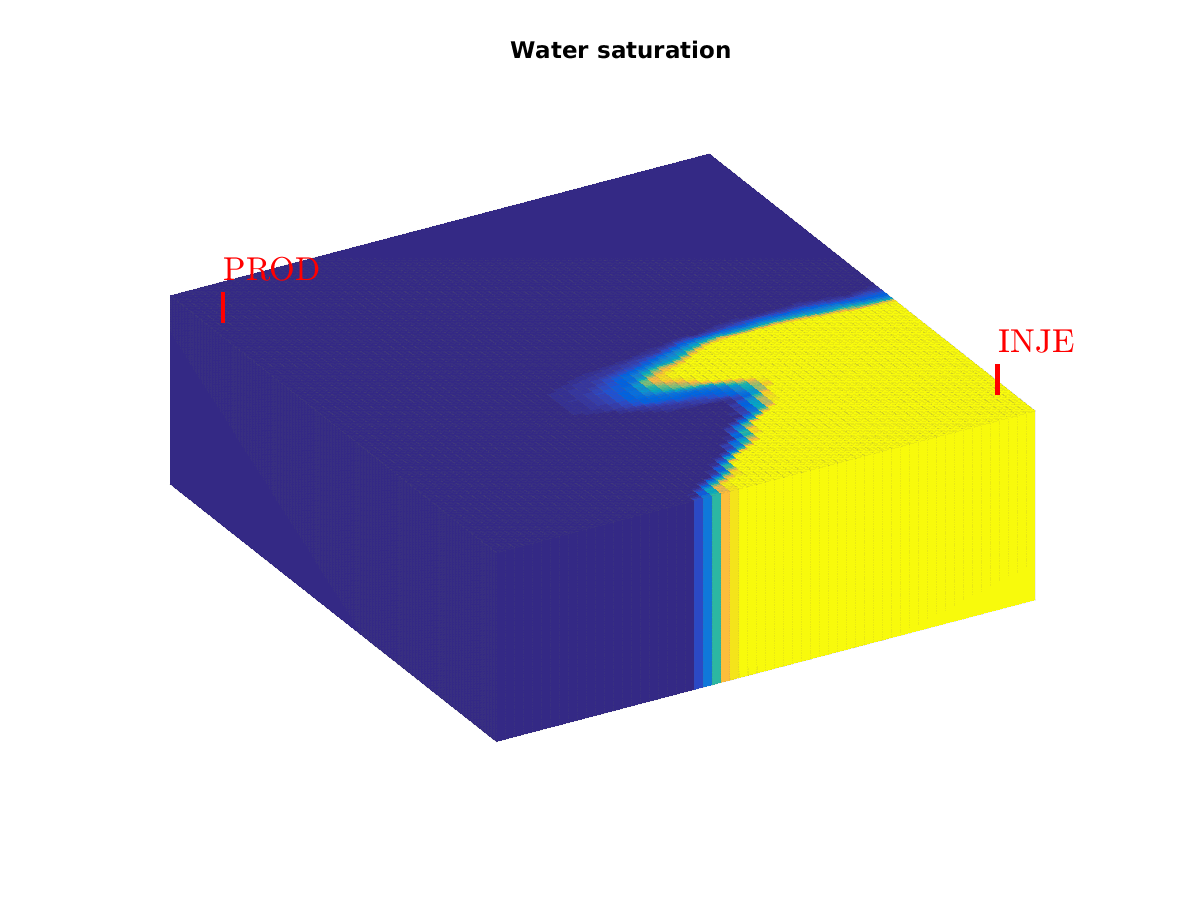
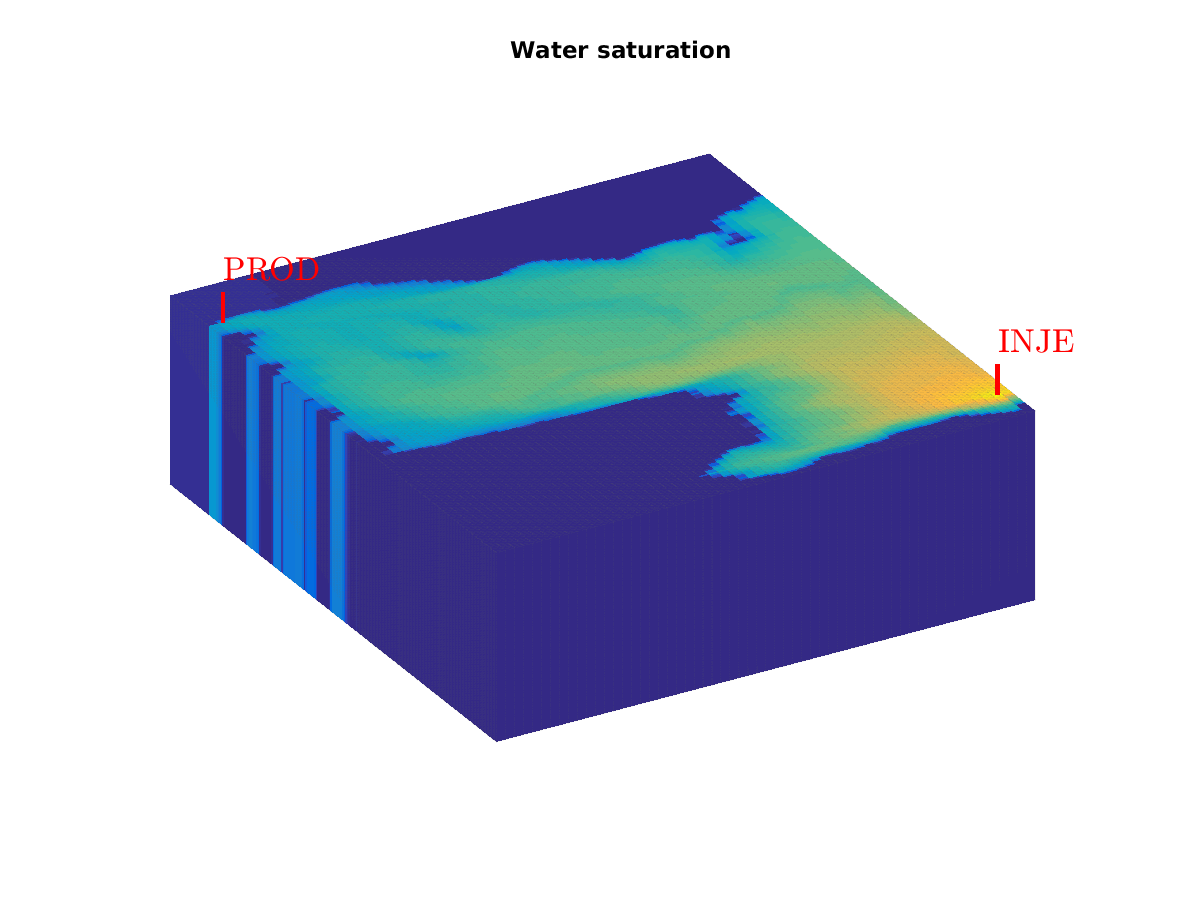
To get a list of the examples, type Polymer example (spe10 layer)Click on image to obtain full-size version.
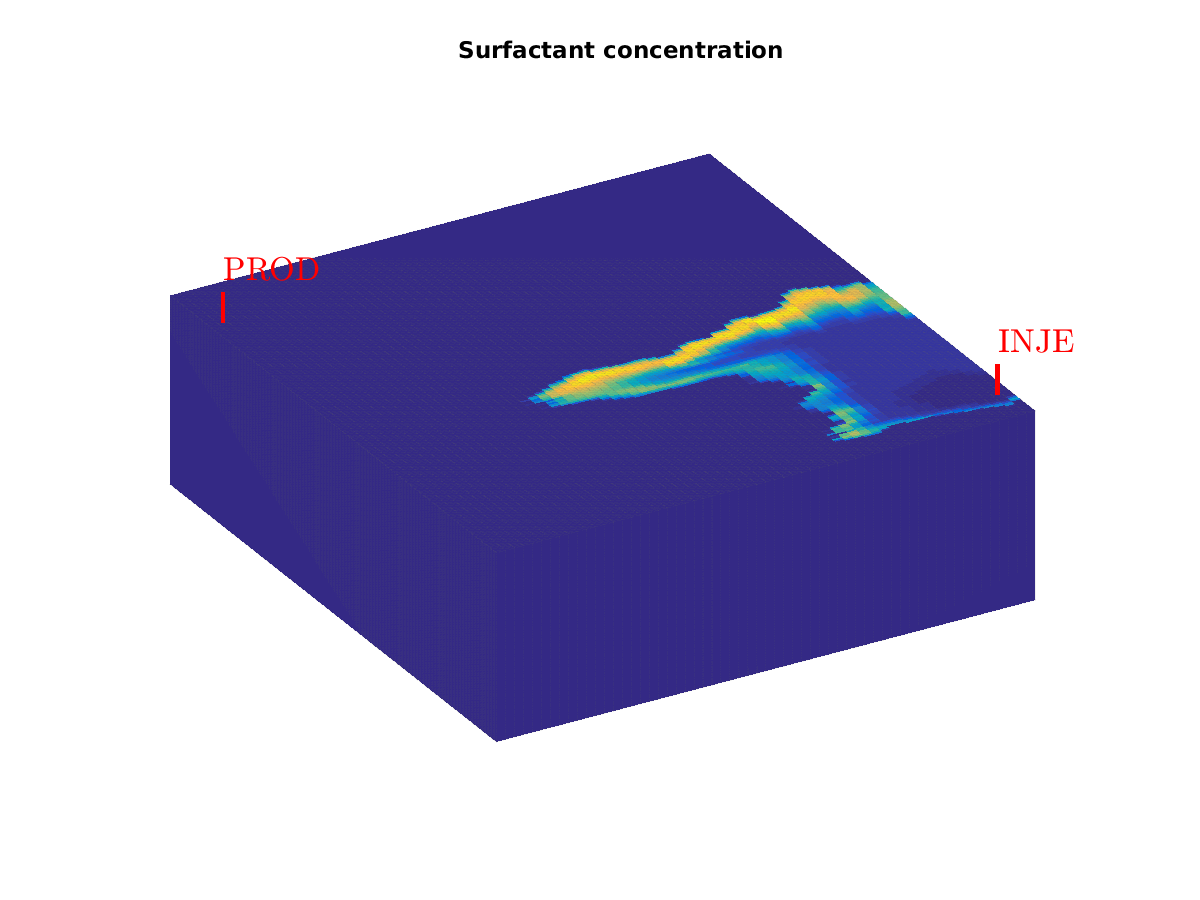
Surfactant example (spe10 layer)
Related references
|
||||||||