Industrial surplus heat-to-power conversion – opportunities and challenges
Brede Hagen, PhD, NTNU
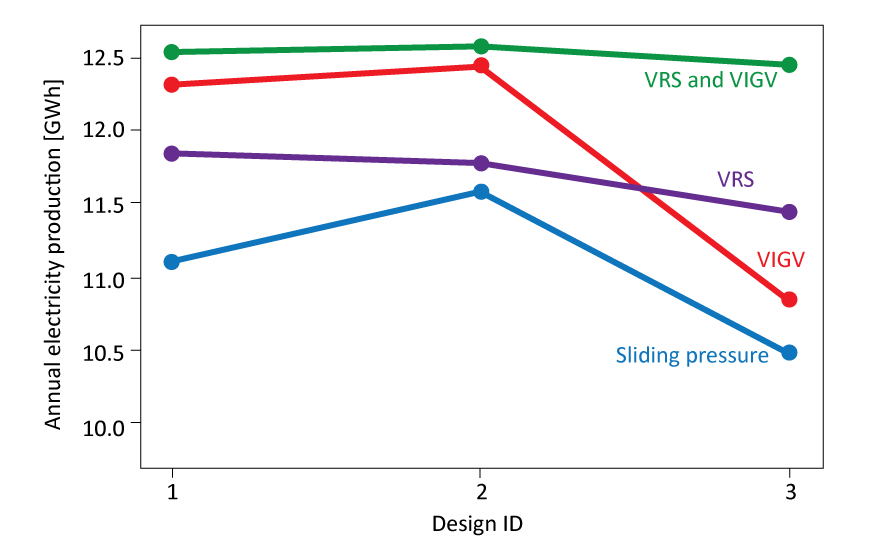
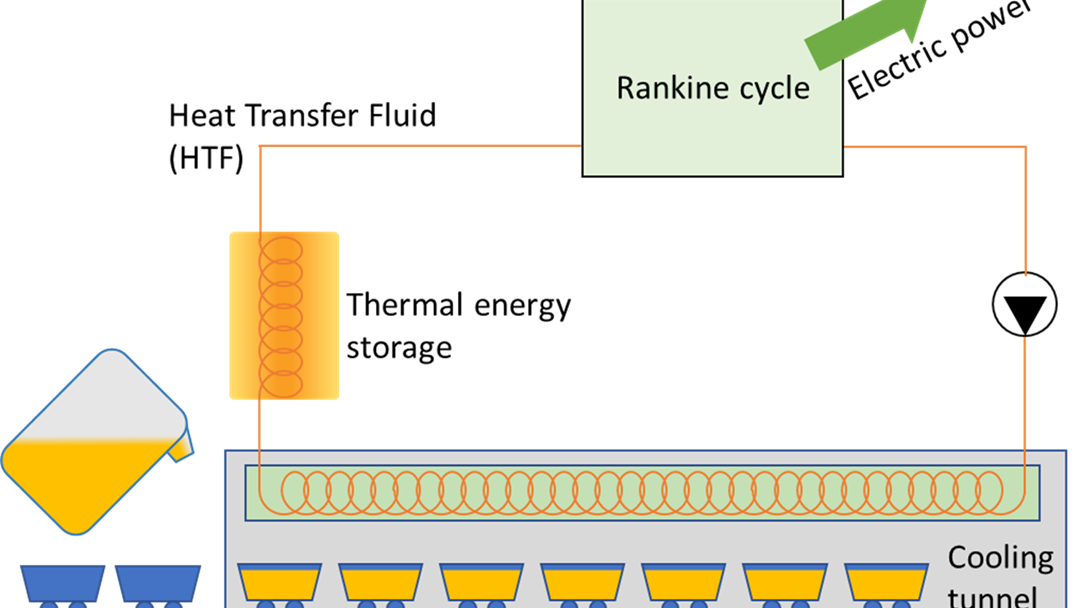
The energy intensive Norwegian industry generates a lot of heat that currently is wasted. One reason for this is the lack of sufficient energy demand near the industrial facilities. This heat, however, could be used by converting it to electric power, because electricity can be transported over long distances. The main challenge for the profitability of heat-to-power systems is that the thermodynamic laws constrain the power output to a small fraction of the heat input. I tried to address this issue by developing methods to design highly efficient heat-to-power conversion systems. These methods were applied to design and analyse a system converting the heat released from the casting process at a ferroalloy plant to power (see figure a). More specifically, three designs were generated and evaluated over a one-year period considering four control strategies (see figure b). The results show that the VRS and VIGV control strategies generate significantly more electricity than the traditional sliding pressure control strategy.