#include <SplineSurface.h>
Inheritance diagram for Go::SplineSurface:

Public Types | ||||
| enum | NormalConeMethod | |||
| Enumerates the method for computing the normal cone. | ||||
Public Member Functions | ||||
| SplineSurface () | ||||
| Creates an uninitialized SplineSurface, which can only be assigned to or read(. | ||||
| template<typename RandomIterator1, typename RandomIterator2, typename RandomIterator3> | ||||
| SplineSurface (int number1, int number2, int order1, int order2, RandomIterator1 knot1start, RandomIterator2 knot2start, RandomIterator3 coefsstart, int dim, bool rational=false) | ||||
| Create a SplineSurface by explicitly providing all spline-related information. | ||||
| template<typename RandomIterator> | ||||
| SplineSurface (const BsplineBasis &basis_u, const BsplineBasis &basis_v, RandomIterator coefsstart, int dim, bool rational=false) | ||||
| Create a SplineSurface by explicitly providing all spline-related information. | ||||
| virtual | ~SplineSurface () | |||
| Virtual destructor, enables safe inheritance. | ||||
| virtual void | read (std::istream &is) | |||
| read object from stream | ||||
| virtual void | write (std::ostream &os) const | |||
| write object to stream | ||||
| virtual BoundingBox | boundingBox () const | |||
| Return the object's bounding box. | ||||
| virtual int | dimension () const | |||
| Return the dimension of the space in which the object lies (usually 2 or 3). | ||||
| void | swap (SplineSurface &other) | |||
| quick swap of two SplineSurface objects with each other | ||||
| virtual ClassType | instanceType () const | |||
| Return the class type identifier of a given, derived instance of GeomObject. | ||||
| virtual SplineSurface * | clone () const | |||
| make a clone of this surface and return a pointer to it (user is responsible for clearing up memory afterwards). | ||||
| virtual const RectDomain & | parameterDomain () const | |||
| Return the parameter domain of the surface. | ||||
| virtual RectDomain | containingDomain () const | |||
| Get a rectangular parameter domain that is guaranteed to contain the surface's parameterDomain(). | ||||
| virtual CurveLoop | outerBoundaryLoop (double degenerate_epsilon=DEFAULT_SPACE_EPSILON) const | |||
| Returns the anticlockwise, outer boundary loop of the surface. | ||||
| virtual std::vector< CurveLoop > | allBoundaryLoops (double degenerate_epsilon=DEFAULT_SPACE_EPSILON) const | |||
| Returns the anticlockwise outer boundary loop of the surface, together with clockwise loops of any interior boundaries, such that the surface always is 'to the left of' the loops. | ||||
| virtual void | point (Point &pt, double upar, double vpar) const | |||
| Evaluates the surface's position for a given parameter pair. | ||||
| virtual void | point (std::vector< Point > &pts, double upar, double vpar, int derivs, bool u_from_right=true, bool v_from_right=true, double resolution=1.0e-12) const | |||
| Evaluates the surface's position and a certain number of derivatives for a given parameter pair. | ||||
| virtual double | startparam_u () const | |||
| Get the start value for the u-parameter. | ||||
| virtual double | startparam_v () const | |||
| Get the start value for the v-parameter. | ||||
| virtual double | endparam_u () const | |||
| Get the end value for the u-parameter. | ||||
| virtual double | endparam_v () const | |||
| Get the end value for the v-parameter. | ||||
| virtual void | normal (Point &n, double upar, double vpar) const | |||
| Evaluates the surface normal for a given parameter pair. | ||||
| DirectionCone | normalCone (NormalConeMethod method) const | |||
| Returns a cone that contains the convex hull of all normalized tangents of the surface. | ||||
| virtual DirectionCone | normalCone () const | |||
| Function that calls normalCone(NormalConeMethod) with method = SederbergMeyers. | ||||
| virtual DirectionCone | tangentCone (bool pardir_is_u) const | |||
| Creates a DirectionCone covering all tangents to this surface along a given parameter direction. | ||||
| virtual CompositeBox | compositeBox () const | |||
| Creates a composite box enclosing the surface. | ||||
| SplineSurface * | normal () const | |||
| Not yet implemented. | ||||
| SplineSurface * | normalSurface () const | |||
Returns the normal surface corresponding to this surface, as described in: Computing normal vector Bezier patches, Przemyslaw Kiciak, Computer Aided Design 18 (2001), 699-710. | ||||
| SplineSurface * | derivSurface (int ider1, int ider2) const | |||
| Get the derivative surface. | ||||
| SplineSurface * | subSurface (double from_upar, double from_vpar, double to_upar, double to_vpar, double fuzzy=DEFAULT_PARAMETER_EPSILON) const | |||
| Get a SplineSurface which represent a part of 'this' SplineSurface. | ||||
| virtual std::vector< boost::shared_ptr< ParamSurface > > | subSurfaces (double from_upar, double from_vpar, double to_upar, double to_vpar, double fuzzy=DEFAULT_PARAMETER_EPSILON) const | |||
| Get the surface(s) obtained by cropping the parameter domain of this surface between given values for the first and second parameter. | ||||
| virtual void | closestPoint (const Point &pt, double &clo_u, double &clo_v, Point &clo_pt, double &clo_dist, double epsilon, const RectDomain *domain_of_interest=NULL, double *seed=0) const | |||
| Iterates to the closest point to pt on the surface. | ||||
| virtual void | closestBoundaryPoint (const Point &pt, double &clo_u, double &clo_v, Point &clo_pt, double &clo_dist, double epsilon, const RectDomain *rd=NULL, double *seed=0) const | |||
| Iterates to the closest point to pt on the boundary of the surface. | ||||
| void | appendSurface (ParamSurface *sf, int join_dir, int continuity, double &dist, bool repar=true) | |||
| Appends a surface to the end of 'this' surface along a specified parameter direction. | ||||
| void | appendSurface (ParamSurface *sf, int join_dir, bool repar=true) | |||
| Short hand function to call appendSurface with C^1 continuity. | ||||
| virtual void | getBoundaryInfo (Point &pt1, Point &pt2, double epsilon, SplineCurve *&cv, SplineCurve *&crosscv, double knot_tol=1e-05) const | |||
| Get the boundary curve segment between two points on the boundary, as well as the cross-tangent curve. | ||||
| void | getBoundaryInfo (double par1, double par2, int bdindex, SplineCurve *&cv, SplineCurve *&crosscv, double knot_tol=1e-05) const | |||
| Get the boundary curve and the outward cross tangent curve between two parameter values on a given boundary. | ||||
| void | getBoundaryIdx (Point &pt1, Point &pt2, double epsilon, int &bdindex, double &par1, double &par2, double knot_tol=1e-05) const | |||
| Given two points on the surface boundary, find the number of the corresponding boundary and the curve parameter of the closest points on this surface boundary. | ||||
| void | getBoundaryIdx (Point &pt1, double epsilon, int &bdindex, double knot_tol=1e-05) const | |||
| ||||
| virtual void | turnOrientation () | |||
| Turns the direction of the normal of the surface. | ||||
| virtual void | swapParameterDirection () | |||
| Swaps the two parameter directions. | ||||
| virtual void | reverseParameterDirection (bool direction_is_u) | |||
| Reverses the direction of the basis in input direction. | ||||
| int | boundaryIndex (Point ¶m_pt1, Point ¶m_pt2) const | |||
| find whether two points are lying on the same surface boundary; if this is the case, return the index of the boundary (as specified in getBoundaryIdx()), else return 1 | ||||
| const BsplineBasis & | basis_u () const | |||
| get a const reference to the BsplineBasis for the first parameter | ||||
| const BsplineBasis & | basis_v () const | |||
| get a const reference to the BsplineBasis for the second parameter | ||||
| const BsplineBasis & | basis (int i) const | |||
| get one of the BsplineBasises of the surface | ||||
| int | numCoefs_u () const | |||
| Query the number of control points along the first parameter direction. | ||||
| int | numCoefs_v () const | |||
| Query the number of control points along the second parameter direction. | ||||
| int | order_u () const | |||
| Query the order of the BsplineBasis for the first parameter. | ||||
| int | order_v () const | |||
| Query the order of the BsplineBasis for the second parameter. | ||||
| bool | rational () const | |||
| Query whether the surface is rational. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::iterator | coefs_begin () | |||
| Get an iterator to the start of the internal array of non-rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::iterator | coefs_end () | |||
| Get an iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of non- rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::const_iterator | coefs_begin () const | |||
| Get a const iterator to the start of the internal array of non-rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::const_iterator | coefs_end () const | |||
| Get a const iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of non-rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::iterator | rcoefs_begin () | |||
| Get an iterator to the start of the internal array of rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::iterator | rcoefs_end () | |||
| Get an iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::const_iterator | rcoefs_begin () const | |||
| Get a const iterator to the start of the internal array of rational control points. | ||||
| std::vector< double >::const_iterator | rcoefs_end () const | |||
| Get a const iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of rational control points. | ||||
| virtual bool | isDegenerate (bool &b, bool &r, bool &t, bool &l, double tolerance) const | |||
| Query whether any of the four boundary curves are degenerate (zero length) within a certain tolerance. | ||||
| void | setParameterDomain (double u1, double u2, double v1, double v2) | |||
| set the parameter domain to a given rectangle | ||||
| void | insertKnot_u (double apar) | |||
| Insert a new knot in the knotvector of the first parameter. | ||||
| void | insertKnot_u (const std::vector< double > &new_knots) | |||
| Insert new knots in the knotvector of the first parameter. | ||||
| void | insertKnot_v (double apar) | |||
| Insert a new knot in the knotvector of the second parameter. | ||||
| void | insertKnot_v (const std::vector< double > &new_knots) | |||
| Insert new knots in the knotvector of the second parameter. | ||||
| void | removeKnot_u (double tpar) | |||
| Remove a knot from the knotvector of the first parameter. | ||||
| void | removeKnot_v (double tpar) | |||
| Remove a knot from the knotvector of the second parameter. | ||||
| void | makeBernsteinKnotsU () | |||
| Inserts knots in the u knot vector, such that all knots have multiplicity order. | ||||
| void | makeBernsteinKnotsV () | |||
| Inserts knots in the v knot vector, such that all knots have multiplicity order. | ||||
| int | numberOfPatches_u () const | |||
| Returns the number of knot intervals in u knot vector. | ||||
| int | numberOfPatches_v () const | |||
| Returns the number of knot intervals in v knot vector. | ||||
| void | raiseOrder (int raise_u, int raise_v) | |||
| Raise the order of the spline surface as indicated by parameters. | ||||
| SplineCurve * | constParamCurve (double parameter, bool pardir_is_u) const | |||
| Generate and return a SplineCurve that represents a constant parameter curve on the surface. | ||||
| void | constParamCurve (double parameter, bool pardir_is_u, SplineCurve *&cv, SplineCurve *&crosscv) const | |||
| Generate and return two SplineCurves, representing a constant parameter curve on the surface as well as it cross-tangent curve. | ||||
| virtual std::vector< boost::shared_ptr< ParamCurve > > | constParamCurves (double parameter, bool pardir_is_u) const | |||
| Get the curve(s) obtained by intersecting the surface with one of its constant parameter curves. | ||||
| SplineCurve * | edgeCurve (int ccw_edge_number) const | |||
| Generate and return a SplineCurve representing one of the surface's four edges. | ||||
| void | interpolate (Interpolator &interpolator1, Interpolator &interpolator2, int num_points1, int num_points2, int dim, const double *param1_start, const double *param2_start, const double *data_start) | |||
| Remake 'this'surface to interpolate (or approximate) a given point grid. | ||||
| void | gridEvaluator (int num_u, int num_v, std::vector< double > &points, std::vector< double > &normals, std::vector< double > ¶m_u, std::vector< double > ¶m_v) const | |||
| Evaluate points and normals on an entire grid, taking computational advantage over calculating all these values simultaneously rather than one-by-one. | ||||
| void | gridEvaluator (int num_u, int num_v, std::vector< double > &points, std::vector< double > ¶m_u, std::vector< double > ¶m_v) const | |||
| Evaluate points on an entire grid, taking computational advantage over calculating all these values simultaneously rather than one-by-one. | ||||
| virtual double | nextSegmentVal (int dir, double par, bool forward, double tol) const | |||
| Determine the parameter value of the start of the 'next segment' from a parameter value, along a given parameter direction. | ||||
Static Public Member Functions | ||||
| static ClassType | classType () | |||
| Return the class type identifier of a given class derived from GeomObject. | ||||
Non-rational B-spline surfaces represented on the form
![\[ \sum_{i=1}^{n_1}\sum_{j=1}^{n_2} P_{i,j} /// B_{i,o_1}(u) B_{j,o_2}(v), \]](form_1.png)
where the B-spline coefficients are stored in a vector called coefs. The coefs is stored as
![\[ P_{0,0}, P_{0,1}, \ldots /// P_{n_1, n_2}, \]](form_2.png)
where 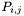 is represented as dim doubles.
is represented as dim doubles.
NURBS surfaces are represented on the form
![\[ \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n_1}\sum_{j=1}^{n_2} w_{i,j}P_{i,j} /// B_{i,o_1}(u) B_{j,o_2}(v)} /// {\sum_{i=1}^{n_1}\sum_{j=1}^{n_2} w_{i,j} B_{i,o_1}(u) B_{j,o_2}(v)} \]](form_4.png)
where 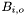 is the i'th non-rational B-spline of order o. The Projected coefficients are stored in the coefs vector, i.e
is the i'th non-rational B-spline of order o. The Projected coefficients are stored in the coefs vector, i.e
![\[ w_{0,0}*P_{0,0}, w_{0,1}*P_{0,1}, \ldots /// w_{n_1, n_2}*P_{n_1, n_2}. \]](form_6.png)
In addition the cefficients for the surface in projective space are kept, i.e
![\[ P_{0,0}, w_{0,0}, P_{0,1}, w_{0,1}, \ldots /// P_{n_1, n_2}, w_{n_1, n_2}. \]](form_7.png)
With this representation surface is in the convex hull of the coefficients stored in coefs both for rational and non rational surfaces.
Definition at line 82 of file SplineSurface.h.
| Go::SplineSurface::SplineSurface | ( | ) | [inline] |
Creates an uninitialized SplineSurface, which can only be assigned to or read(.
..) into.
Definition at line 87 of file SplineSurface.h.
Referenced by clone().
| Go::SplineSurface::SplineSurface | ( | int | number1, | |
| int | number2, | |||
| int | order1, | |||
| int | order2, | |||
| RandomIterator1 | knot1start, | |||
| RandomIterator2 | knot2start, | |||
| RandomIterator3 | coefsstart, | |||
| int | dim, | |||
| bool | rational = false | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Create a SplineSurface by explicitly providing all spline-related information.
| number1 | number of control points along the u-parameter | |
| number2 | number of control points along the v-parameter | |
| order1 | BsplineBasis order along the u-parameter | |
| order2 | BsplineBasis order along the v-parameter | |
| knot1start | pointer to the array describing the knotvector for the u-parameter | |
| knot2start | pointer to the array describing the knotvector for the v-parameter | |
| coefsstart | pointer to the array where the control points are consecutively stored. The storage order is such that control points along the u-parameter have the shortest stride (stored right after each other). If the surface is rational, pay attention to the comments below. | |
| dim | dimension of the space in which the surface lies (usually 3). | |
| rational | Specify whether the surface is rational or not. If the surface is rational, coefficients must be in the following format: wP1 wP2 .... wPdim w. Ie. a (dim+1)-dimensional form. (This is the same form that is used within SISL). |
Definition at line 118 of file SplineSurface.h.
References rational().
| Go::SplineSurface::SplineSurface | ( | const BsplineBasis & | basis_u, | |
| const BsplineBasis & | basis_v, | |||
| RandomIterator | coefsstart, | |||
| int | dim, | |||
| bool | rational = false | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Create a SplineSurface by explicitly providing all spline-related information.
| basis_u | the BsplineBasis to be used along the u-direction | |
| basis_v | the BsplineBasis to be used along the v-direction | |
| coefsstart | pointer to the array where the control points are consecutively stored. The storage order is such that control points along the u-parameter have the shortest stride (stored right after each other). If the surface is rational, pay attention to the comments below. | |
| dim | dimension of the space in which the surface lies (usually 3). | |
| rational | Specify whether the surface is rational or not. If the surface is rational, coefficients must be in the following format: wP1 wP2 .... wPdim w. Ie. a (dim+1)-dimensional form. (This is the same form that is used within SISL). |
Definition at line 161 of file SplineSurface.h.
References basis_u(), basis_v(), Go::BsplineBasis::numCoefs(), and rational().
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::read | ( | std::istream & | is | ) | [virtual] |
read object from stream
| is | stream from which object is read |
Implements Go::Streamable.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::read().
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::write | ( | std::ostream & | os | ) | const [virtual] |
write object to stream
| os | stream to which object is written |
Implements Go::Streamable.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::write().
| virtual SplineSurface* Go::SplineSurface::clone | ( | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
make a clone of this surface and return a pointer to it (user is responsible for clearing up memory afterwards).
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Definition at line 213 of file SplineSurface.h.
References SplineSurface().
| virtual const RectDomain& Go::SplineSurface::parameterDomain | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Return the parameter domain of the surface.
This may be a simple rectangular domain (RectDomain) or any other subclass of Domain (such as GoCurveBoundedDomain, found in the sisl_dependent module).
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual RectDomain Go::SplineSurface::containingDomain | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get a rectangular parameter domain that is guaranteed to contain the surface's parameterDomain().
It may be the same. There is no guarantee that this is the smallest domain containing the actual domain.
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual CurveLoop Go::SplineSurface::outerBoundaryLoop | ( | double | degenerate_epsilon = DEFAULT_SPACE_EPSILON |
) | const [virtual] |
Returns the anticlockwise, outer boundary loop of the surface.
| degenerate_epsilon | edges whose length is smaller than this value are ignored. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::outerBoundaryLoop().
| virtual std::vector<CurveLoop> Go::SplineSurface::allBoundaryLoops | ( | double | degenerate_epsilon = DEFAULT_SPACE_EPSILON |
) | const [virtual] |
Returns the anticlockwise outer boundary loop of the surface, together with clockwise loops of any interior boundaries, such that the surface always is 'to the left of' the loops.
| degenerate_epsilon | edges whose length is smaller than this value are ignored. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::allBoundaryLoops().
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::point | ( | Point & | pt, | |
| double | upar, | |||
| double | vpar | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Evaluates the surface's position for a given parameter pair.
| pt | the result of the evaluation is written here | |
| upar | the first parameter | |
| vpar | the second parameter |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::point().
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::point | ( | std::vector< Point > & | pts, | |
| double | upar, | |||
| double | vpar, | |||
| int | derivs, | |||
| bool | u_from_right = true, |
|||
| bool | v_from_right = true, |
|||
| double | resolution = 1.0e-12 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Evaluates the surface's position and a certain number of derivatives for a given parameter pair.
| pts | the vector containing the evaluated values. Its size must be set by the user prior to calling this function, and should be equal to (derivs+1) * (derivs+2) / 2. Upon completion of the function, its first entry is the surface's position at the given parameter pair. Then, if 'derivs' > 0, the two next entries will be the surface tangents along the first and second parameter direction. The next three entries are the second- and cross derivatives, in the order (du2, dudv, dv2), and similar for even higher derivatives. | |
| upar | the first parameter | |
| vpar | the second parameter | |
| derivs | number of requested derivatives | |
| u_from_right | specify whether derivatives along the first parameter are to be calculated from the right ('true', default) or from the left ('false') | |
| v_from_right | specify whether derivatives along the second parameter are to be calculated from the right ('true', default) or from the left ('false') | |
| resolution | tolerance used when determining whether parameters are located at special values of the parameter domain (in particualar; knot values in case of spline objects. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual double Go::SplineSurface::startparam_u | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the start value for the u-parameter.
| virtual double Go::SplineSurface::startparam_v | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the start value for the v-parameter.
| virtual double Go::SplineSurface::endparam_u | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the end value for the u-parameter.
| virtual double Go::SplineSurface::endparam_v | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Get the end value for the v-parameter.
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::normal | ( | Point & | n, | |
| double | upar, | |||
| double | vpar | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Evaluates the surface normal for a given parameter pair.
| n | the computed normal will be written to this variable | |
| upar | the first parameter | |
| vpar | the second parameter |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::normal().
| DirectionCone Go::SplineSurface::normalCone | ( | NormalConeMethod | method | ) | const |
Returns a cone that contains the convex hull of all normalized tangents of the surface.
Note: It is an overestimate.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::normalCone().
| virtual DirectionCone Go::SplineSurface::normalCone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Function that calls normalCone(NormalConeMethod) with method = SederbergMeyers.
Needed because normalCone() is virtual! (Inherited from ParamSurface).
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual DirectionCone Go::SplineSurface::tangentCone | ( | bool | pardir_is_u | ) | const [virtual] |
Creates a DirectionCone covering all tangents to this surface along a given parameter direction.
| pardir_is_u | if 'true', then the DirectionCone will be defined on basis of the surface's tangents along the first parameter direction. Otherwise the second parameter direction will be used. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::tangentCone().
| virtual CompositeBox Go::SplineSurface::compositeBox | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Creates a composite box enclosing the surface.
The composite box consists of an inner and an edge box. The inner box is supposed to be made from the interior of the surface, while the edge box is made from the boundary curves. The default implementation simply makes both boxes identical to the regular bounding box.
Reimplemented from Go::ParamSurface.
Referenced by Go::CompositeSurface::compositeBox().
| SplineSurface* Go::SplineSurface::normalSurface | ( | ) | const |
Returns the normal surface corresponding to this surface, as described in:
Computing normal vector Bezier patches, Przemyslaw Kiciak, Computer Aided Design 18 (2001), 699-710.
| SplineSurface* Go::SplineSurface::derivSurface | ( | int | ider1, | |
| int | ider2 | |||
| ) | const |
Get the derivative surface.
Expresses the i,j-th derivative of a spline surface as a spline surface. Ported from sisl routine s1386.
| ider1 | what derivative to use along the u parameter | |
| ider2 | what derivative to use along the v parameter |
| SplineSurface* Go::SplineSurface::subSurface | ( | double | from_upar, | |
| double | from_vpar, | |||
| double | to_upar, | |||
| double | to_vpar, | |||
| double | fuzzy = DEFAULT_PARAMETER_EPSILON | |||
| ) | const |
Get a SplineSurface which represent a part of 'this' SplineSurface.
| from_upar | start value for u-parameter in the sub-surface to be generated | |
| from_vpar | start value for v-parameter in the sub-surface to be generated | |
| to_upar | end value for u-parameter in the sub-surface to be generated | |
| to_vpar | end value for v-parameter in the sub-surface to be generated | |
| fuzzy | tolerance used to determine whether given parameter values are located directly knot values. |
| virtual std::vector<boost::shared_ptr<ParamSurface> > Go::SplineSurface::subSurfaces | ( | double | from_upar, | |
| double | from_vpar, | |||
| double | to_upar, | |||
| double | to_vpar, | |||
| double | fuzzy = DEFAULT_PARAMETER_EPSILON | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Get the surface(s) obtained by cropping the parameter domain of this surface between given values for the first and second parameter.
In general, for surfaces with no interior holes, the result will be one surface; however, for surfaces with interior holes, the result might be several disjoint surfaces.
| from_upar | lower value for the first parameter in the subdomain | |
| from_vpar | lower value for the second parameter in the subdomain | |
| to_upar | upper value for the first parameter in the subdomain | |
| to_vpar | upper value for the second parameter in the subdomain | |
| fuzzy | tolerance used when determining intersection with interior boundaries |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::closestPoint | ( | const Point & | pt, | |
| double & | clo_u, | |||
| double & | clo_v, | |||
| Point & | clo_pt, | |||
| double & | clo_dist, | |||
| double | epsilon, | |||
| const RectDomain * | domain_of_interest = NULL, |
|||
| double * | seed = 0 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Iterates to the closest point to pt on the surface.
| pt | the point to find the closest point to | |
| clo_u | u parameter of the closest point | |
| clo_v | v parameter of the closest point | |
| clo_pt | the geometric position of the closest point | |
| clo_dist | the distance between pt and clo_pt | |
| epsilon | parameter tolerance (will in any case not be higher than sqrt(machine_precision) x magnitude of solution | |
| domain_of_interest | pointer to parameter domain in which to search for closest point. If a NULL pointer is used, the entire surface is searched. | |
| seed | pointer to parameter values where iteration starts. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::closestBoundaryPoint | ( | const Point & | pt, | |
| double & | clo_u, | |||
| double & | clo_v, | |||
| Point & | clo_pt, | |||
| double & | clo_dist, | |||
| double | epsilon, | |||
| const RectDomain * | rd = NULL, |
|||
| double * | seed = 0 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Iterates to the closest point to pt on the boundary of the surface.
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| void Go::SplineSurface::appendSurface | ( | ParamSurface * | sf, | |
| int | join_dir, | |||
| int | continuity, | |||
| double & | dist, | |||
| bool | repar = true | |||
| ) |
Appends a surface to the end of 'this' surface along a specified parameter direction.
The knotvector and control point grid of 'this' surface will be extended, and the degree will be raised if necessary. Note that there will be side-effects on the other surface; its order might be raised, its knotvector will become k-regular and reparametrized, one of its edges will be moved to coincide with an edge of 'this' surface, etc.
| sf | the surface to append to 'this' surface | |
| join_dir | the parameter direction along which to extend 'this' surface by appending the 'sf' surface. If it is equal to 1, we will extend the surface along the u-parameter; if it equals 2, we will extend the surface along the v-parameter. | |
| continuity | the desired level of continuity at the transition between the two surfaces (can be from -1 to order()). The higher the value, the more the surfaces will have to be locally modified around the seam. | |
| dist | upon function return, this variable will hold the estimated maximum distorsion after the 'smoothing' of the seam in order to achieve the desired continuity. | |
| repar | The parametrization of the concerned parameter in the other surface will always be shifted so that it starts where the parametrization of 'this' surface ends. However, if 'repar' is set to 'true', it will also be scaled as a function of position of control points close to the transition. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::appendSurface | ( | ParamSurface * | sf, | |
| int | join_dir, | |||
| bool | repar = true | |||
| ) |
Short hand function to call appendSurface with C^1 continuity.
| sf | the surface to append to 'this' surface | |
| join_dir | the parameter direction along which to extend 'this' surface by appending the 'sf' surface. If it is equal to 1, we will extend the surface along the u-parameter; if it equals 2, we will extend the surface along the v-parameter. | |
| repar | The parametrization of the concerned parameter in the other surface will always be shifted so that it starts where the parametrization of 'this' surface ends. However, if 'repar' is set to 'true', it will also be scaled as a function of position of control points close to the transition. |
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::getBoundaryInfo | ( | Point & | pt1, | |
| Point & | pt2, | |||
| double | epsilon, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | cv, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | crosscv, | |||
| double | knot_tol = 1e-05 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Get the boundary curve segment between two points on the boundary, as well as the cross-tangent curve.
If the given points are not positioned on the same boundary (within a certain tolerance), no curves will be created.
| pt1 | the first point on the boundary, given by the user | |
| pt2 | the second point on the boundary, given by the user | |
| epsilon | the tolerance used when determining whether the given points are lying on a boundary, and if they do, whether they both lie on the same boundary. | |
| cv | upon return, this will point to a newly created curve representing the boundary curve between 'pt1' and 'pt2'. The user assumes ownership of this object and is responsible for its deletion. No curve is created if the given points are not found to lie on the same boundary. | |
| crosscv | upon return, this will point to a newly created curve representing the cross-boundary curve between 'pt1' and 'pt2' The user assumes ownership of this object and is responsible for its deletion. The direction is outwards from the surface. No curve is created if the given points are not found to lie on the same boundary. | |
| knot_tol | tolerance used when working with the knot-vector, to specify how close a parameter value must be to a knot in order to be considered 'on' the knot. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| void Go::SplineSurface::getBoundaryInfo | ( | double | par1, | |
| double | par2, | |||
| int | bdindex, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | cv, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | crosscv, | |||
| double | knot_tol = 1e-05 | |||
| ) | const |
Get the boundary curve and the outward cross tangent curve between two parameter values on a given boundary.
| par1 | first parameter along the boundary | |
| par2 | second parameter along the boundary | |
| bdindex | index of the boundary in question. The boundaries are indexed as in getBoundaryIdx(). | |
| cv | returns a pointer to a generated SplineCurve representing the boundary between the given parameters. The user assumes ownership and is responsible for deletion. | |
| crosscv | returns a pointer to a generated SplineCurve representing the cross tangent curve between the given parameters on the boundary. The direction is outwards from the surface. The user assumes ownership and is responsible for deletion. | |
| knot_tol | tolerance used when working with the knot-vector, to specify how close a parameter value must be to a knot in order to be considered 'on' the knot. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::getBoundaryIdx | ( | Point & | pt1, | |
| Point & | pt2, | |||
| double | epsilon, | |||
| int & | bdindex, | |||
| double & | par1, | |||
| double & | par2, | |||
| double | knot_tol = 1e-05 | |||
| ) | const |
Given two points on the surface boundary, find the number of the corresponding boundary and the curve parameter of the closest points on this surface boundary.
Ordering of boundaries:
/// 1
/// ----------------------
/// | |
/// 2 | | 3
/// v | |
/// ^ ----------------------
/// |-> u 0
/// | pt1 | point in geometry space | |
| pt2 | point in geometry space | |
| epsilon | geometric tolerance | |
| bdindex | if the two points are on a common boundary, the index of the boundary, otherwise -1. | |
| par1 | if bdindex is 0 or 1, the u parameter of pt1, otherwise the v parameter. | |
| par2 | if bdindex is 0 or 1, the u parameter of pt2, otherwise the v parameter. | |
| knot_tol | tolerance used when working with the knot-vector, to specify how close a parameter value must be to a knot in order to be considered 'on' the knot. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::getBoundaryIdx | ( | Point & | pt1, | |
| double | epsilon, | |||
| int & | bdindex, | |||
| double | knot_tol = 1e-05 | |||
| ) | const |
| pt1 | the point we want to find the boundary for |
| epsilon | the geometric distance the point can have from a boundary and still be considered as laying on the boundary. | |
| bdindex | the index of the boundary on which the point lies. If the point was found not to lie on any boundary, the value will be -1. | |
| knot_tol | tolerance used when working with the knot-vector, to specify how close a parameter value must be to a knot in order to be considered 'on' the knot. |
| virtual void Go::SplineSurface::reverseParameterDirection | ( | bool | direction_is_u | ) | [virtual] |
Reverses the direction of the basis in input direction.
| direction_is_u | if 'true', the first parameter direction will be reversed, otherwise, the second parameter direction will be reversed |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
find whether two points are lying on the same surface boundary; if this is the case, return the index of the boundary (as specified in getBoundaryIdx()), else return 1
| const BsplineBasis& Go::SplineSurface::basis_u | ( | ) | const [inline] |
get a const reference to the BsplineBasis for the first parameter
Definition at line 492 of file SplineSurface.h.
Referenced by SplineSurface().
| const BsplineBasis& Go::SplineSurface::basis_v | ( | ) | const [inline] |
get a const reference to the BsplineBasis for the second parameter
Definition at line 497 of file SplineSurface.h.
Referenced by SplineSurface().
| const BsplineBasis& Go::SplineSurface::basis | ( | int | i | ) | const [inline] |
get one of the BsplineBasises of the surface
| i | specify whether to return the BsplineBasis for the first parameter (0), or for the second parameter (1). |
Definition at line 504 of file SplineSurface.h.
| int Go::SplineSurface::numCoefs_u | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Query the number of control points along the first parameter direction.
Definition at line 509 of file SplineSurface.h.
References Go::BsplineBasis::numCoefs().
| int Go::SplineSurface::numCoefs_v | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Query the number of control points along the second parameter direction.
Definition at line 514 of file SplineSurface.h.
References Go::BsplineBasis::numCoefs().
| int Go::SplineSurface::order_u | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Query the order of the BsplineBasis for the first parameter.
Definition at line 519 of file SplineSurface.h.
References Go::BsplineBasis::order().
| int Go::SplineSurface::order_v | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Query the order of the BsplineBasis for the second parameter.
Definition at line 524 of file SplineSurface.h.
References Go::BsplineBasis::order().
| bool Go::SplineSurface::rational | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Query whether the surface is rational.
Definition at line 529 of file SplineSurface.h.
Referenced by SplineSurface().
| std::vector<double>::iterator Go::SplineSurface::coefs_begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Get an iterator to the start of the internal array of non-rational control points.
Definition at line 536 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::iterator Go::SplineSurface::coefs_end | ( | ) | [inline] |
Get an iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of non- rational control points.
Definition at line 543 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::const_iterator Go::SplineSurface::coefs_begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get a const iterator to the start of the internal array of non-rational control points.
Definition at line 550 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::const_iterator Go::SplineSurface::coefs_end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get a const iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of non-rational control points.
Definition at line 557 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::iterator Go::SplineSurface::rcoefs_begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Get an iterator to the start of the internal array of rational control points.
Definition at line 564 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::iterator Go::SplineSurface::rcoefs_end | ( | ) | [inline] |
Get an iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of rational control points.
Definition at line 571 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::const_iterator Go::SplineSurface::rcoefs_begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get a const iterator to the start of the internal array of rational control points.
Definition at line 578 of file SplineSurface.h.
| std::vector<double>::const_iterator Go::SplineSurface::rcoefs_end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Get a const iterator to the one-past-end position of the internal array of rational control points.
Definition at line 585 of file SplineSurface.h.
| virtual bool Go::SplineSurface::isDegenerate | ( | bool & | b, | |
| bool & | r, | |||
| bool & | t, | |||
| bool & | l, | |||
| double | tolerance | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Query whether any of the four boundary curves are degenerate (zero length) within a certain tolerance.
In the below, we refer to 'u' as the first parameter and 'v' as the second.
| b | 'true' upon return of function if the boundary (v = v_min) is degenerate | |
| r | 'true' upon return of function if the boundary (v = v_max) is degenerate | |
| t | 'true' upon return of function if the boundary (u = u_min) is degenerate | |
| l | 'true' upon return of function if the boundary (u = u_max) is degenerate | |
| tolerance | boundaries are considered degenerate if their length is shorter than this value, given by the user |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| void Go::SplineSurface::setParameterDomain | ( | double | u1, | |
| double | u2, | |||
| double | v1, | |||
| double | v2 | |||
| ) |
set the parameter domain to a given rectangle
| u1 | new min. value of first parameter span | |
| u2 | new max. value of first parameter span | |
| v1 | new min. value of second parameter span | |
| v2 | new max. value of second parameter span |
| void Go::SplineSurface::insertKnot_u | ( | double | apar | ) |
Insert a new knot in the knotvector of the first parameter.
| apar | the parameter value at which a new knot will be inserted |
| void Go::SplineSurface::insertKnot_u | ( | const std::vector< double > & | new_knots | ) |
Insert new knots in the knotvector of the first parameter.
| new_knots | a vector containing the parameter values of the new knots to insert. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::insertKnot_v | ( | double | apar | ) |
Insert a new knot in the knotvector of the second parameter.
| apar | the parameter value at which a new knot will be inserted |
| void Go::SplineSurface::insertKnot_v | ( | const std::vector< double > & | new_knots | ) |
Insert new knots in the knotvector of the second parameter.
| new_knots | a vector containing the parameter values of the new knots to insert. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::removeKnot_u | ( | double | tpar | ) |
Remove a knot from the knotvector of the first parameter.
| tpar | the parameter value of the knot to be removed |
| void Go::SplineSurface::removeKnot_v | ( | double | tpar | ) |
Remove a knot from the knotvector of the second parameter.
| tpar | the parameter value of the knot to be removed. |
| int Go::SplineSurface::numberOfPatches_u | ( | ) | const |
Returns the number of knot intervals in u knot vector.
| int Go::SplineSurface::numberOfPatches_v | ( | ) | const |
Returns the number of knot intervals in v knot vector.
| void Go::SplineSurface::raiseOrder | ( | int | raise_u, | |
| int | raise_v | |||
| ) |
Raise the order of the spline surface as indicated by parameters.
| raise_u | the order of the BsplineBasis associated with the first parameter will be raised this many times. | |
| raise_v | the order of the BsplineBasis associated with the second parameter will be raised this many times. |
| SplineCurve* Go::SplineSurface::constParamCurve | ( | double | parameter, | |
| bool | pardir_is_u | |||
| ) | const |
Generate and return a SplineCurve that represents a constant parameter curve on the surface.
| parameter | value of the fixed parameter | |
| pardir_is_u | 'true' if the first parameter is the running parameter, 'false' otherwise. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::constParamCurve | ( | double | parameter, | |
| bool | pardir_is_u, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | cv, | |||
| SplineCurve *& | crosscv | |||
| ) | const |
Generate and return two SplineCurves, representing a constant parameter curve on the surface as well as it cross-tangent curve.
| parameter | value of the fixed parameter | |
| pardir_is_u | 'true' if the first parameter is the running parameter, 'false' otherwise. | |
| cv | upon function completion, 'cv' will point to a newly constructed SplineCurve representing the specified constant parameter curve. It is the user's responsibility to delete it when it is no longer needed. | |
| crosscv | upon function completion, 'crosscv' will point to a newly constructed SplineCurve representing the cross-tangent curve of the specified constant parameter curve. It is the user's reponsibility to delete it when it is no longer needed. |
| virtual std::vector< boost::shared_ptr<ParamCurve> > Go::SplineSurface::constParamCurves | ( | double | parameter, | |
| bool | pardir_is_u | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Get the curve(s) obtained by intersecting the surface with one of its constant parameter curves.
For surfaces without holes, this will be the parameter curve itself; for surfaces with interior holes this may be a collection of several, disjoint curves.
| parameter | parameter value for the constant parameter (either u or v) | |
| pardir_is_u | specify whether the moving parameter (as opposed to the constant parameter) is the first ('true') or the second ('false') one. |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
| SplineCurve* Go::SplineSurface::edgeCurve | ( | int | ccw_edge_number | ) | const |
Generate and return a SplineCurve representing one of the surface's four edges.
| ccw_edge_number | indicates which edge the user requests.
/// 0 -> bottom edge
/// 1 -> right edge
/// 2 -> top edge
/// 3 -> left edge |
| void Go::SplineSurface::interpolate | ( | Interpolator & | interpolator1, | |
| Interpolator & | interpolator2, | |||
| int | num_points1, | |||
| int | num_points2, | |||
| int | dim, | |||
| const double * | param1_start, | |||
| const double * | param2_start, | |||
| const double * | data_start | |||
| ) |
Remake 'this'surface to interpolate (or approximate) a given point grid.
| interpolator1 | Interpolator to apply to the first parameter direction | |
| interpolator2 | Interpolator to apply to the second parameter direction | |
| num_points1 | number of points to interpolate along the first parameter direction | |
| num_points2 | number of points to interpolate along the second parameter direction | |
| dim | dimension of the points to interpolate (usually 3) | |
| param1_start | pointer to the start of the input grid's parametrization along the first parameter | |
| param2_start | pointer to the start of the input grid's parametrization along the second parameter | |
| data_start | pointer to the start of the storage array for the data point grid to interpolate |
| void Go::SplineSurface::gridEvaluator | ( | int | num_u, | |
| int | num_v, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | points, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | normals, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | param_u, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | param_v | |||
| ) | const |
Evaluate points and normals on an entire grid, taking computational advantage over calculating all these values simultaneously rather than one-by-one.
| num_u | number of values to evaluate along first parameter direction | |
| num_v | number of values to evaluate along second parameter direction | |
| points | upon function return, this vector holds all the evaluated points | |
| normals | upon function return, this vector holds all the evaluated normals | |
| param_u | upon function return, this vector holds all the numerical values for the first parameter where evaluation has taken place | |
| param_v | upon function return, this vector holds all the numerical values for the second parameter where evaluation has taken place. |
| void Go::SplineSurface::gridEvaluator | ( | int | num_u, | |
| int | num_v, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | points, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | param_u, | |||
| std::vector< double > & | param_v | |||
| ) | const |
Evaluate points on an entire grid, taking computational advantage over calculating all these values simultaneously rather than one-by-one.
| num_u | number of values to evaluate along first parameter direction | |
| num_v | number of values to evaluate along second parameter direction | |
| points | upon function return, this vector holds all the evaluated points | |
| param_u | upon function return, this vector holds all the numerical values for the first parameter where evaluation has taken place | |
| param_v | upon function return, this vector holds all the numerical values for the second parameter where evaluation has taken place. |
| virtual double Go::SplineSurface::nextSegmentVal | ( | int | dir, | |
| double | par, | |||
| bool | forward, | |||
| double | tol | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Determine the parameter value of the start of the 'next segment' from a parameter value, along a given parameter direction.
A 'segment' is here defined as a parameter interval in which there will be no discontinuities in derivatives or other artifacts. For spline objects, a segment will typically be the interval between two consecutive, non-coincident knots.
| dir | the parameter direction in which we search for the next segment (0 or 1) | |
| par | the parameter value starting from which we search for the start value of the next segment | |
| forward | define whether we shall move forward ('true') or backwards when searching along this parameter | |
| tol | tolerance used for determining whether the 'par' is already located on the next segment value |
Implements Go::ParamSurface.
 1.5.1
1.5.1