 or
or  , where connectivity is explicitly defined.
More...
, where connectivity is explicitly defined.
More...
#include <PrExplicitConnectivity.h>
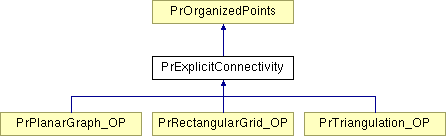
Inheritance diagram for PrExplicitConnectivity:

Public Member Functions | |
| virtual int | findNumFaces () const |
| count the number of faces in the graph | |
| void | findFace (int i, int j, std::vector< int > &neighbours, std::vector< int > &face) const |
| Find the face of the graph which lies to the left of the directed edge whose end points are the node i and its j-th neighbour. | |
| int | findGenus () const |
| Compute the genus of the planar graph. | |
| bool | isTriangulation () const |
| Check if the planar graph is a triangulation. | |
| virtual void | printXYZFaces (std::ostream &os) const |
| Print out the faces of the graph. | |
| virtual void | printXYZFacesML (std::ostream &os) const |
| Print out the faces of the graph, ML format. | |
| virtual void | printXYZFacesVRML (std::ostream &os) const |
| Print out the faces of the graph, VRML format. | |
| virtual void | printUVFaces (std::ostream &os) const |
| Print out the faces of the parameterization. | |
| void | findNextEdgeInFace (int &i, int &j, std::vector< int > &neighbours) const |
| Find the next edge in the face which lies to the left of the directed edge whose end points are the node 'i' and its j-th neighbour. | |
| virtual void | printInfo (std::ostream &os) const |
| Print general information about this PrOrganizedPoints object (number of nodes, etc.). | |
| virtual void | printTexture (std::ostream &os) const |
 or
or  , where connectivity is explicitly defined.
, where connectivity is explicitly defined.
The two common examples are a triangulation and a topologically rectangular grid. What differentiates this class from PrOrganizedPoints is that for PrExplicitConnectivity, it is possible to directly identify faces. The methods in this class are used by PrParametrize.
Definition at line 48 of file PrExplicitConnectivity.h.
| void PrExplicitConnectivity::findFace | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j, | |||
| std::vector< int > & | neighbours, | |||
| std::vector< int > & | face | |||
| ) | const |
Find the face of the graph which lies to the left of the directed edge whose end points are the node i and its j-th neighbour.
The nodes of the face, starting with i, will be filled out in the list vector<int> face. The vector<int> neighbours is used for temporarily storing neighbours (for efficiency when calling this routine many times).
| i | the index of the node specifying the directed edge | |
| j | the 'j'th neighbour of 'i' will be the second node specifying the edge |
| neighbours | a temporary vector holding the neighbours of the last node examined by the implementation (might not always be needed; its presence in the parameter list is mainly an efficiency issue). | |
| face | upon function return, will contain the indexes of the nodes in the requested face (anticlockwise order). |
Referenced by findNumFaces(), and isTriangulation().
| void PrExplicitConnectivity::findNextEdgeInFace | ( | int & | i, | |
| int & | j, | |||
| std::vector< int > & | neighbours | |||
| ) | const |
Find the next edge in the face which lies to the left of the directed edge whose end points are the node 'i' and its j-th neighbour.
| i | the index of the node specifying the directed edge. Upon function return, it will contain the corresponding value for the next edge in the face. | |
| j | the 'j'th neighbour of 'i' will be the second node specifying the edge. Upon function return, it will contain the contain the corresponding value for the next edge in the face. | |
| neighbours | when calling the function, this vector should contain the indexes of the neighbour nodes of node 'i'. Upon function return, it will contain the corresponding value for the next node in the face. |
 1.5.1
1.5.1