ANALYST: Advanced Analytics on Smart Data
Improved processing power and decreased costs of sensors and data storage has created a data deluge: so much data is generated that extracting useful information from the data is like finding a needle in a haystack. In ANALYST, we will expand the state of the art of Big Data Analytics, turning Big Data into Smart Data using innovative techniques for Locally Refined Spline modelling.
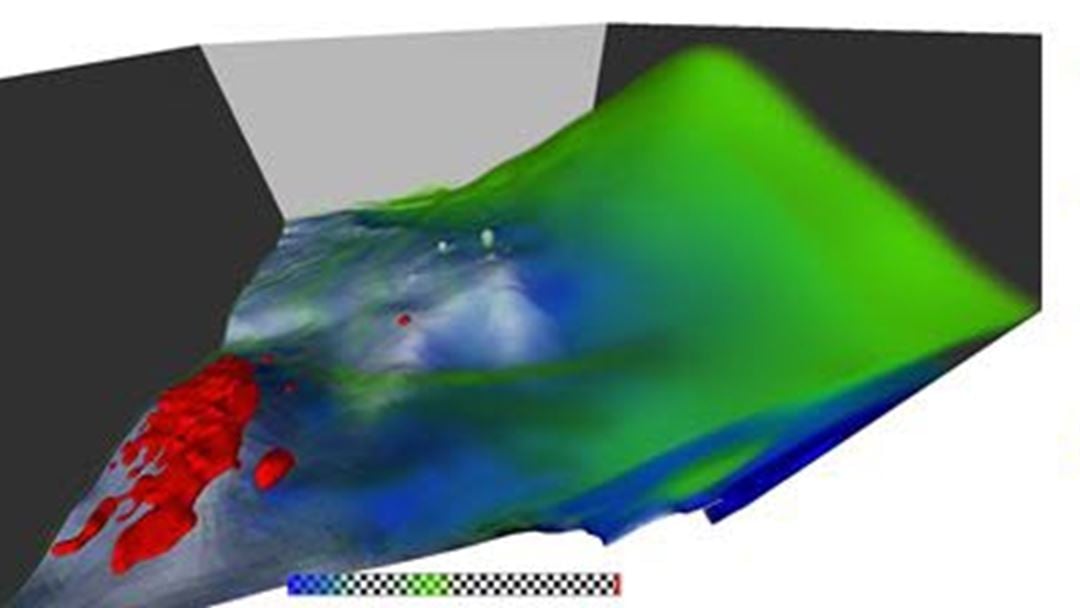
The challenge of managing, investigating, and visualizing big datasets is not new in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM). From seismic surveys of new oil fields, through Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations of waterpower turbines, to large-scale meteorological forecasts, we have always faced limitations in computing power and storage capacity. Recent developments in BDA offer a new set of tools for overcoming these challenges. However, there are significant new challenges that arise from the structural differences between most STEM data and the unstructured textual data typical in classical Big Data applications. STEM data such as simulation results and sonar surveys has a spatial structure, displays complex behaviour, and comes in inconveniently large chunks.
In order to address these challenges, ANALYST has used Locally Refined (LR-) spline data modelling to turn Big STEM Data into Smart Data. In early implementations of LR-spline algorithms in 2D and 3D, we have seen their potential as compact interactive models for visual and quantitative analytics on big spatial datasets. The data structure of LR-splines is directly related to the spatial distribution and local variation in the data, enabling efficient hardware-accelerated interrogation and visualization. By splitting the data into tiles, approximating each tile independently, and stitching these approximations back together, we have an extremely versatile and parallelizable approach, well suited for Big Data infrastructures. This tiling-and-stitching procedure can be achieved for LR-spline models in any dimension. We can therefore include time and other relevant variables in a compact, interactive, multi-scale, higher order, locally refined model.
ANALYST has provided a research platform to bring the theoretical foundation of LR-splines up to a level where their full potential can be explored, combining BDA and AI to provide advanced analytics on the LR-spline model. While the focus will be on data from applications in the STEM fields, the resulting algorithms have a wider applicability, providing highly scalable complex modelling tools for Big Data Analytics.
Some Analyst publications:
- Gael Kermarrec; Vibeke Skytt, Tor Dokken, Optimal Surface Fitting of Point Clouds Using Local Refinement, SpringerBriefs in Earth System Sciences Series, Januar 2023. Open Acces (Link to Book)
- Gael Kermarrec; Vibeke Skytt, Tor Dokken, Surface approximation of coastal regions: LR B-spline for detection of deformation pattern, 2022, ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2022. Link to paper (Open Access)
-
Vibeke Skytt, Gael Kermarrec, and Tor Dokken, LR B-splines to approximate bathymetry datasets: An improved statistical criterion to judge the goodness of fit, International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2022, Link to paper (Open Access)
-
Vibeke Skytt, Tor Dokken, Scattered Data Approximation by LR B-Spline Surfaces: A Study on Refinement Strategies for Efficient Approximation, in Geometric Challenges in Isogeometric Analysis, Springer Nature, 2022, Link to paper (Open Access)
-
Ivar Stangeby, Tor Dokken, Properties of Spline Spaces Over Structured Hierarchical Box Partitions, in Conference on Isogeometric Analysis and Applications IGAA 2018, Springer 2021, Link to Information on paper.
-
Agnar Georg Peder Muntingh, Nainamalai Varatharan, Ivar Haugaløkken Stangeby, Binary segmentation of medical images using implicit spline representations and deep learning, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2021, Link to Information on paper.
-
Konstantinos Gavriil, Agnar Georg Peder Muntingh, Oliver Joseph David Barrowclough, Void Filling of Digital Elevation Models With Deep Generative Models, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. Link to Information on paper.
Prosjektdeltakere
Tor Dokken
Research Manager / Chief Scientist- Name
- Tor Dokken
- Title
- Research Manager / Chief Scientist
- Phone
- +47 93 05 87 10
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS
Oliver Barrowclough
Senior Research Scientist- Name
- Oliver Barrowclough
- Title
- Senior Research Scientist
- Phone
- +47 94 03 26 99
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS
Georg Muntingh
Senior Research Scientist- Name
- Georg Muntingh
- Title
- Senior Research Scientist
- Phone
- +47 41 00 37 28
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS
Sverre Briseid
Research Scientist- Name
- Sverre Briseid
- Title
- Research Scientist
- Phone
- +47 40 22 33 90
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS
Vibeke Skytt
Senior Research Scientist- Name
- Vibeke Skytt
- Title
- Senior Research Scientist
- Phone
- +47 92 46 35 27
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS
Konstantinos Gavriil
Research Scientist- Name
- Konstantinos Gavriil
- Title
- Research Scientist
- Phone
- +47 41 20 33 95
- Department
- Mathematics and Cybernetics
- Office
- Oslo
- Company
- SINTEF AS